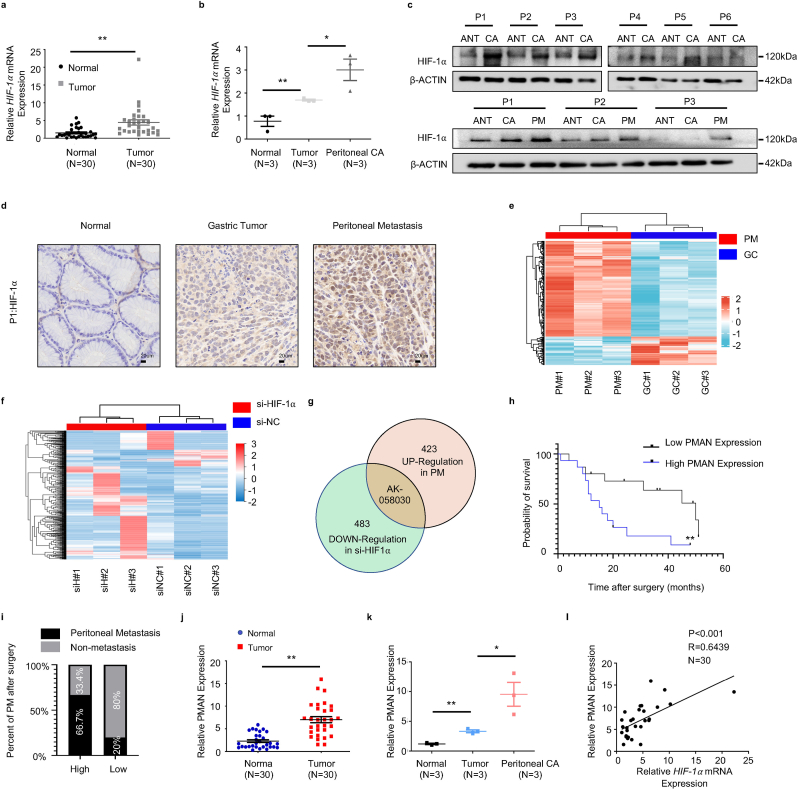
Fig. 1.
PMAN is highly expressed in gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis and is highly correlated with the patient's prognosis.aHIF-1α mRNA expressions in 30 pairs GC samples. Mean ± SD is shown. Statistical analysis was conducted using Student's t-test. bHIF-1α mRNA expressions in 3 pairs GC peritoneal metastasis samples. Mean ± SD is shown. Statistical analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA. c HIF-1α expression levels in 6 pairs GC samples and 3 pairs GC peritoneal metastasis samples. d Immunohistochemistry was used to analyze up-regulated HIF-1α expressions in paired GC peritoneal metastasis samples. Scale bar, 20 μm e Analysis of the expression of lncRNAs in GC peritoneal metastasis by lncRNA-microarrays. f Analysis of the expression of lncRNAs in HIF-1α knockdown AGS cells by lncRNA-seq. g AK-058030 is highly expressed in GC peritoneal metastasis samples and its expression decreases with knockdown of HIF-1α. h Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival rates correlated with PMAN expression (high/low expression) in GC. Error bars, SD. i In the postoperative follow-up data, the relationship between the occurrence of PM and the expression of PMAN (high/low expression) in GC patients j PMAN expressions in 30 pairs GC samples. Mean ± SD is shown. Statistical analysis was conducted using Student's t-test. k PMAN expressions in 3 pairs GC peritoneal metastasis samples. Mean ± SD is shown. Statistical analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA. l Correlations between HIF-1α mRNA levels and PMAN levels in GC. R-values and P-values were used via Pearson's correlation analysis. Mean ± SD are shown. Ns = nonsignificant (p > 0.05), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.