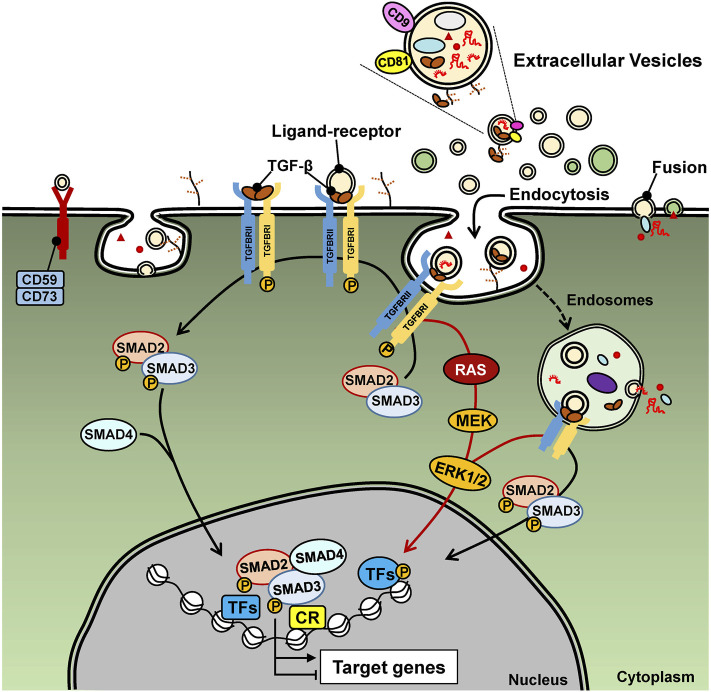
FIGURE 2.
TGF-β signaling. Extracellular TGF-β (usually deposited in the ECM) and here shown as free mature TGF-β, binds to the type II and type I receptors on the cell surface, which signal via inter-receptor trans-phosphorylation. The type I receptor phosphorylates SMAD2 and SMAD3 that results in their oligomerization with SMAD4. The ligand-bound receptors also activate RAS, MEK, ERK and other (not shown) protein kinase signaling pathways. EV-associated TGF-β signals in the same manner, yet the ligand is presented from the surface of EVs, as endocytosis of these EVs is in progress. The signaling proteins, SMADs and MAPKs regulate gene transcription via direct binding to DNA (SMADs) and via phosphorylation of transcription factors (TF) and association with chromatin regulatory protein (CR). MiRNAs and lncRNAs are illustrated as EV cargo and may be viewed with potential caution as to the ability of EVs to deliver functional RNAs to the recipient cells that can affect TGF-β signaling either in a positive or negative manner.