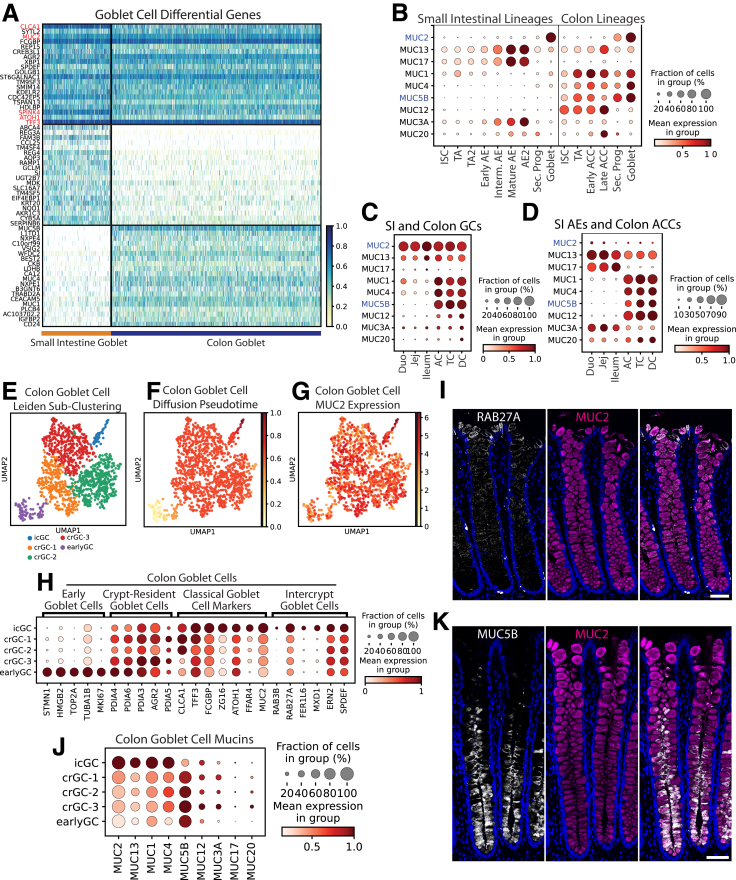
Figure 10.
Goblet cells. (A) Heatmap of DEGs in GCs vs other lineages (top; red: classic markers), SI vs colon GCs (middle), and colon vs SI GCs (bottom). (B) Dotplot showing expression of the 9 highest-expressed mucins across GCs and proliferative and absorptive lineages of the SI and colon (blue: gel-forming mucins). (C) Dotplot showing the 9 highest-expressed mucins across GCs by region. (D) Dotplot showing expression of the 9 highest-expressed mucins in all absorptive enterocytes and colonocytes by intestinal region. (E) Leiden subclustering of colon GCs. (F) Diffusion pseudotime of colon GCs. (G) UMAP of MUC2 expression in colon GCs. (H) Dotplot showing markers of murine GC subpopulations in the human colon GC subclusters defined in panel E. (I) Immunofluorescence staining for protein expression of RAB27A (white), MUC2 (magenta), and nuclei (blue) in human colon (2-μm optical slice). (J) Dotplot showing expression of mucins in colonic icGCs, crypt-resident goblet cells (crGCs), and early goblet cells. (K) Immunofluorescence staining for protein expression of MUC5B (white), MUC2 (magenta), and nuclei (blue) in human colon (2-μm optical slice). Scale bars: 50 μm. UMAP, Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection; Duo, Duodenum; Jej, Jejunum.