FIGURE 5.
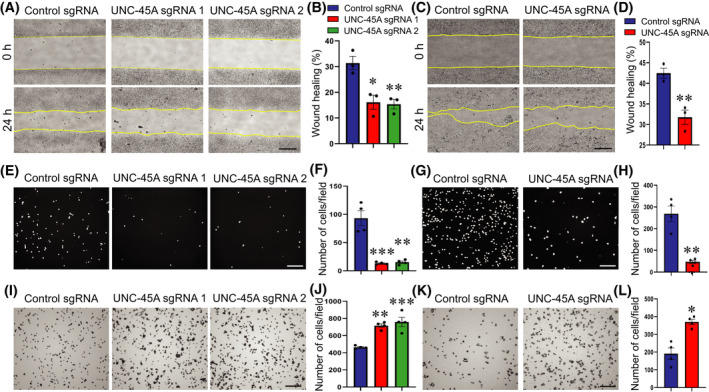
Loss of UNC‐45A expression inhibits epithelial cell migration and increases cell extracellular matrix adhesion. (A–D) Wound healing assay in control and UNC‐45A‐depleted HT‐29cf8 (A, B) and SK‐CO15 (C, D) cell monolayers. Representative wound images (A, C) and quantification of wound closure (B, D) are shown. (E–H) Boyden Chamber migration assay of control and UNC‐45A‐knockout HT‐29cf8 (E, F) and SK‐CO15 (G, H) cells. Representative images of migrated cells stained with DAPI (E, G) and quantification of transfilter cell migration (F, H) are shown. (I–L) Collagen I matrix adhesion assay of control and UNC‐45A‐knockout HT‐29cf8 (I, J) and SK‐CO15 (K, L) cells. Representative images of attached cells (I, K) and quantification of cells adhered after 30 min incubation (J, L) are shown. Mean ± SE (n = 3); *p < .05, **p < .005; ***p < .0005, compared with the control sgRNA groups. Scale bars, 200 µm. (A–D) Data are representative of three independent experiments, (E–K) data are representative of two experiments
