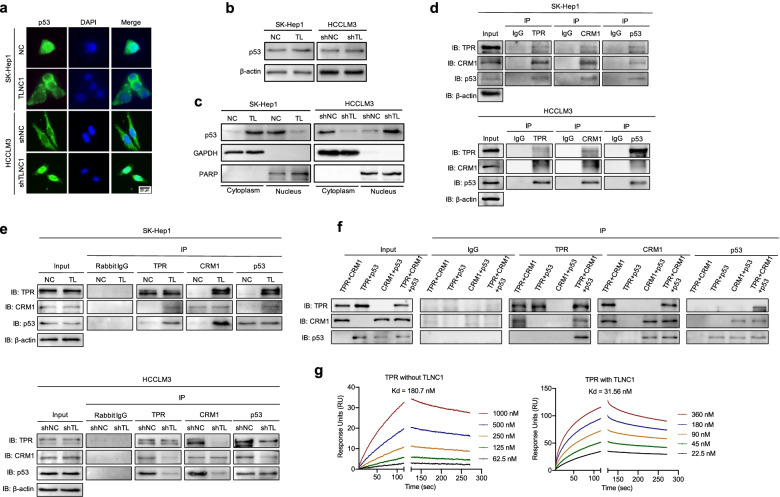
Fig. 6.
TLNC1 represses nuclear translocation of p53 through interaction with TPR. a p53 expression in indicated SK-Hep1 and HCCLM3 cells, as detected by an immunofluorescence assay. The merged images show overlays of p53 (green) and nuclear staining by DAPI (blue); scale bar: 20 μm. b Immunoblot analysis of p53 in indicated SK-Hep1 and HCCLM3 cells. c p53 expression in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, as detected by immunoblot analysis. GAPDH was used as a loading control for the cytoplasmic fraction, and PARP was used as a loading control for the nuclear fraction. d Co-immunoprecipitation among TPR, CRM1 and p53 in SK-Hep1 and HCCLM3 cells, as detected by immunoblot analysis. e Co-immunoprecipitation among TPR, CRM1 and p53 in indicated SK-Hep1 (TLNC1 overexpression) and HCCLM3 (TLNC1 knockdown) cells, as detected by immunoblot analysis. f Co-immunoprecipitation among recombinant TPR, CRM1 and p53 proteins, as detected by immunoblot analysis. The data are the representative of three independent experiments. g Surface plasmon resonance analysis of the binding of CRM1 with increasing concentrations of recombinant TPR in the presence or absence of TLNC1