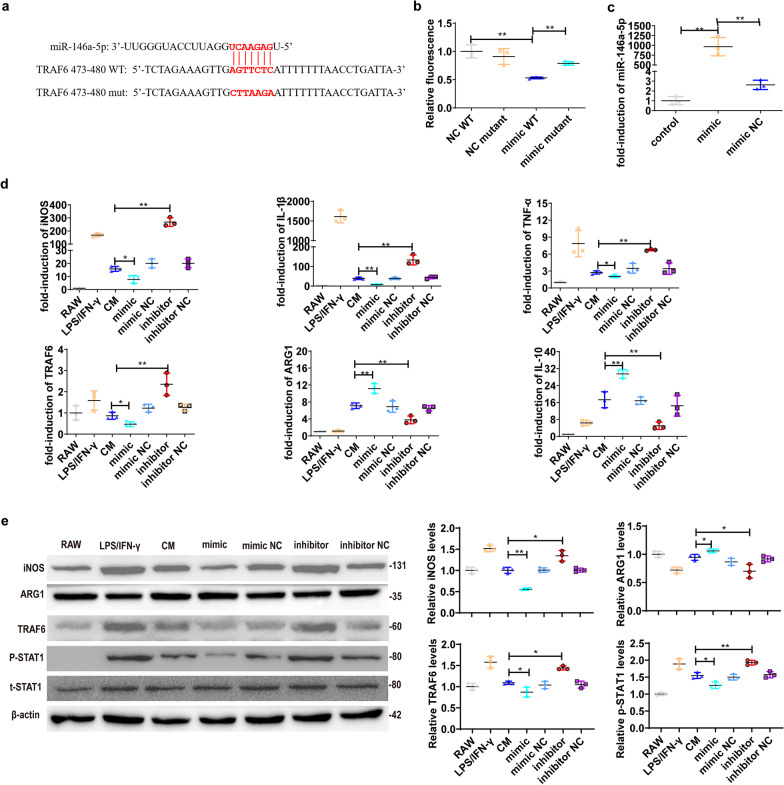
Fig. 5.
UC-MSC-derived miR-146a-5p targets TRAF6 and facilitates M2 macrophage polarization in RAW264.7. a TargetScan predicted miR-146a-5p binding sites in the 3′UTR at 473–480 sites of TRAF6 and the corresponding designed mutation site. b Luciferase activity was measured in HEK293T cells were co-transfected with miR-146a-5p mimic or miR-146a-5p NC and luciferase reporter plasmids containing wild-type or mutant. c The expression of miR-146a-5p in control UC-MSCs, miR-146a-5p mimic transfected UC-MSCs and miR-146a-5p mimic NC transfected UC-MSCs. The miR-146a-5p mimic, miR-146a-5p inhibitor and their negative controls were transfected into UC-MSCs, and the CM was collected to treat RAW264.7. d Relative mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines and M1/M2 macrophage markers including iNOS, IL-1β, TNF-α, TRAF6, ARG1, and IL-10 in the control RAW264.7, LPS/IFN-γ-stimulated RAW264.7 and LPS/IFN-γ-stimulated RAW264.7 treated with the indicated CM. e Relative protein expression and semi-quantitative analysis of iNOS, ARG1, TRAF6, and p-STAT1 in RAW264.7. Data presented as mean ± SD in each group. Results in vitro are representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01