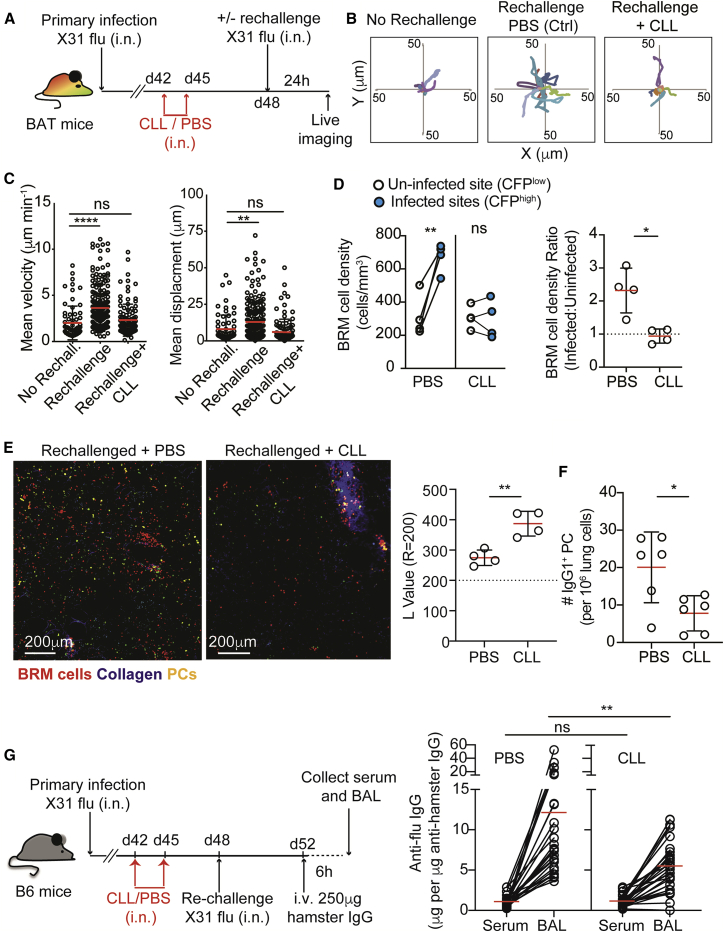
Figure 6.
Depletion of alveolar macrophages leads to loss of resident memory B cell mobilization and plasma cell differentiation in infected lungs
(A) Experimental setup for (A–C).
(B) Plots of BRM cell tacks migrating from a common origin.
(C) Mean velocities and displacements of BRM cells. Data are pooled from 4 independent experiments with a total of 3–4 mice per group.
(D) BRM density in uninfected and infected sites of mice treated as in (A) and infected with CFP-S-Flu. Right, data represented as the fold-change difference. Data are pooled from 4 independent experiments.
(E) PCs 4 days post rechallenge in PBS- and CLL-treated mice. Left, representative images using TPLSM. Right, L values of PCs at r = 200. Plots are pooled from 4 independent experiments.
(F) Lung PCs analyzed by flow cytometry 4 days post rechallenge of mice treated with CLL or PBS liposomes as in (A). Data represent one of 3 independent experiments.
(G) Left, experimental design. Right, ELISA of anti-influenza (flu) ratios between concentrations of anti-influenza and hamster antibodies measured in the serum and BAL of PBS and CLL-treated rechallenged mice. Each circle represents one mouse. Data are pooled from 3 independent experiments performed. Lines indicate matched data from individual animals.
Statistical analysis were made using Kruskal-Wallis tests (C), a paired t test (D, left plot), unpaired t tests (E and F), and Mann-Whitney U test (D, right plot, and G). Error bars represent SD. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. See also Figure S5.