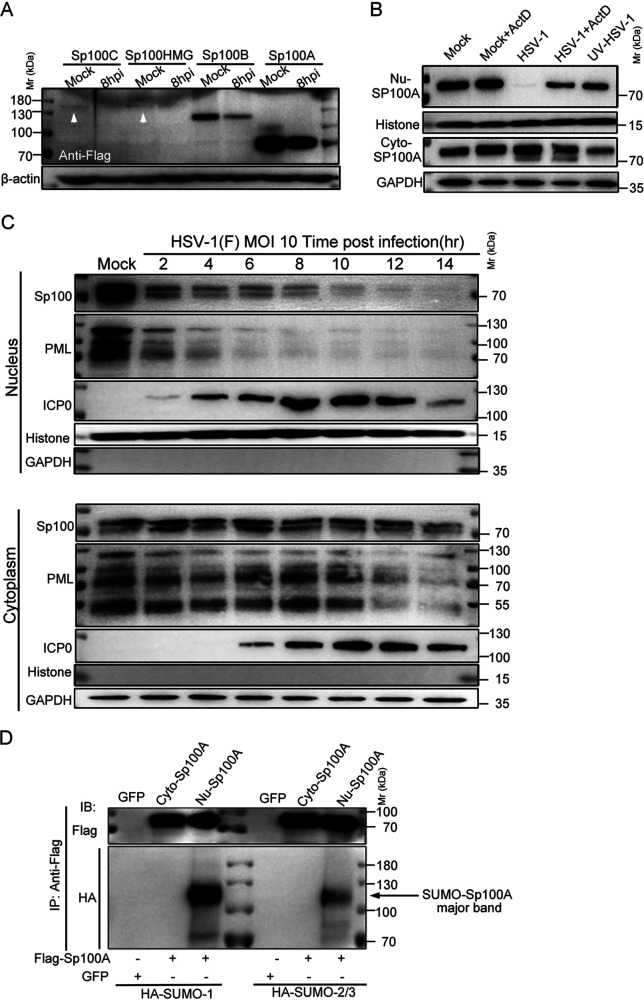
FIG 3.
Cytosolic Sp100 remained stable during HSV-1 infection. (A) HEp-2 cells were transfected with plasmids coding for individual Sp100 isoforms (Flag tagged) for 24 h and mock infected or infected with HSV-1 at an MOI of 5. At 8 hpi, cell lysates were collected and immunoblotted with antibodies against Flag and β-actin. (B) HEp-2+A cells were nontreated, treated with 5 μg/mL actinomycin D (ActD) for 2 h, infected with HSV-1 at an MOI of 10 in the presence or absence of ActD, or inoculated with UV-inactivated HSV-1 of the same amount. Subcellular fractions of different groups of cells were collected at 6 hpi, and the protein levels of Sp100A in the nucleus (Nu-Sp100A) and the cytoplasm (Cyto-Sp100A) were analyzed by immunoblotting with polyclonal anti-Sp100 antibody. Histone and GAPDH served as loading controls. (C) HEp-2 cells were infected with HSV-1 at an MOI of 10. Subcellular fractions were collected at the indicated time points postinfection, and protein levels of Sp100, PML, and ICP0 were analyzed by immunoblotting with polyclonal anti-Sp100 antibody and anti-PML and anti-ICP0 antibodies. Histone and GAPDH served as markers for subcellular compartments. Cytosolic Sp100A was loaded at portions and exposed under conditions similar to those of nuclear Sp100. (D) HEp-2 cells were cotransfected with plasmids coding for Flag-Sp100A or GFP and plasmids coding for HA-SUMO1 or HA-SUMO2/3, as indicated. At 24 h posttransfection, Sp100A was immunoprecipitated (IP) down from the cytosolic and nuclear compartments by anti-Flag antibody and immunoblotted (IB) with antibodies against the HA tag and Flag tag. Fivefold more total cytosolic immunoprecipitated lysate was loaded so that cytosolic Sp100A was at an amount similar to that of nuclear Sp100A. The arrow points to the SUMOylated Sp100A band.