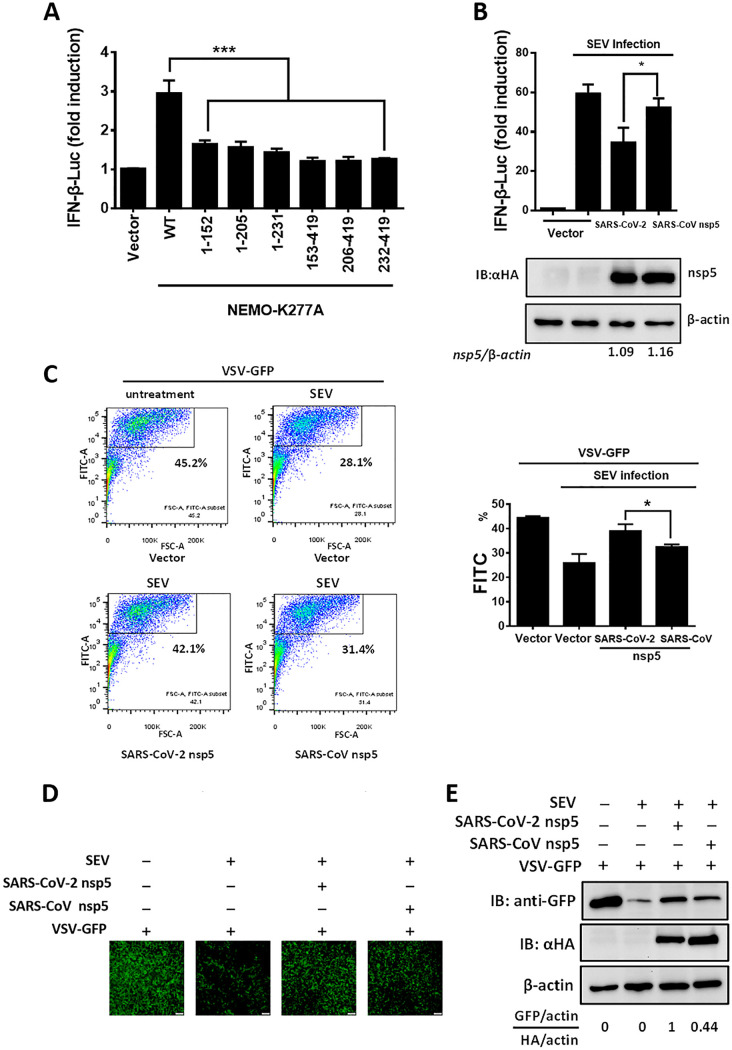
FIG 5.
SARS-CoV-2 nsp5 suppresses IFN-β production more efficiently than SARS-CoV nsp5. (A) We transfected 0.4 μg of plasmid expressing NEMO-truncated mutants (NEMO-K277A [1-152], NEMO-K277A [1-205], NEMO-K277A [1-231], NEMO-K277A [153-419], NEMO-K277A [206-419], and NEMO-K277A [232-419]) along with IFN-β reporter plasmid and pRL-TK plasmid into HEK-293T cells for 28 h. The cells were then lysed and evaluated by dual-luciferase assay. (B) HEK-293T cells seeded in a 24-well plate were cotransfected with equal amounts of expression vectors encoding SARS-CoV-2 nsp5 (0.015 μg) or SARS-CoV nsp5 (0.06 μg) along with IFN-β reporter plasmid and pRL-TK plasmid. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were infected with Sendai virus (SEV). The cells were collected 16 h after SEV infection and used in luciferase assays to assess the expression of the IFN-β reporter. Expression of nsp5 was analyzed by Western blotting. Bands were quantitated by densitometry using ImageJ software, and nsp5 expression was standardized to that of β-actin. (C) HEK-293T cells seeded in a 24-well plate were transfected with equal amounts of plasmid encoding SARS-CoV-2 nsp5 and SARS-CoV nsp5 for 24 h, followed by SEV infection for 12 h. The cell supernatants were then collected, treated with UV irradiation, and added to a new 24-well plate HEK-293T cells for 24 h. The IFN-treated cells were then inoculated with VSV-GFP for 12 h, followed by the detection of GFP-positive cells by flow cytometry. (D and E) Cells were treated as described in panel C. The GFP expression in cells treated with cell supernatants from cells transfected with the indicated plasmid was detected by fluorescence microscopy (D) and Western blot assay (E). The nsp5 expression of the transfected cells was also detected in Western blot assay. All groups were performed in triplicate, and the results represent means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001.