FIG 2.
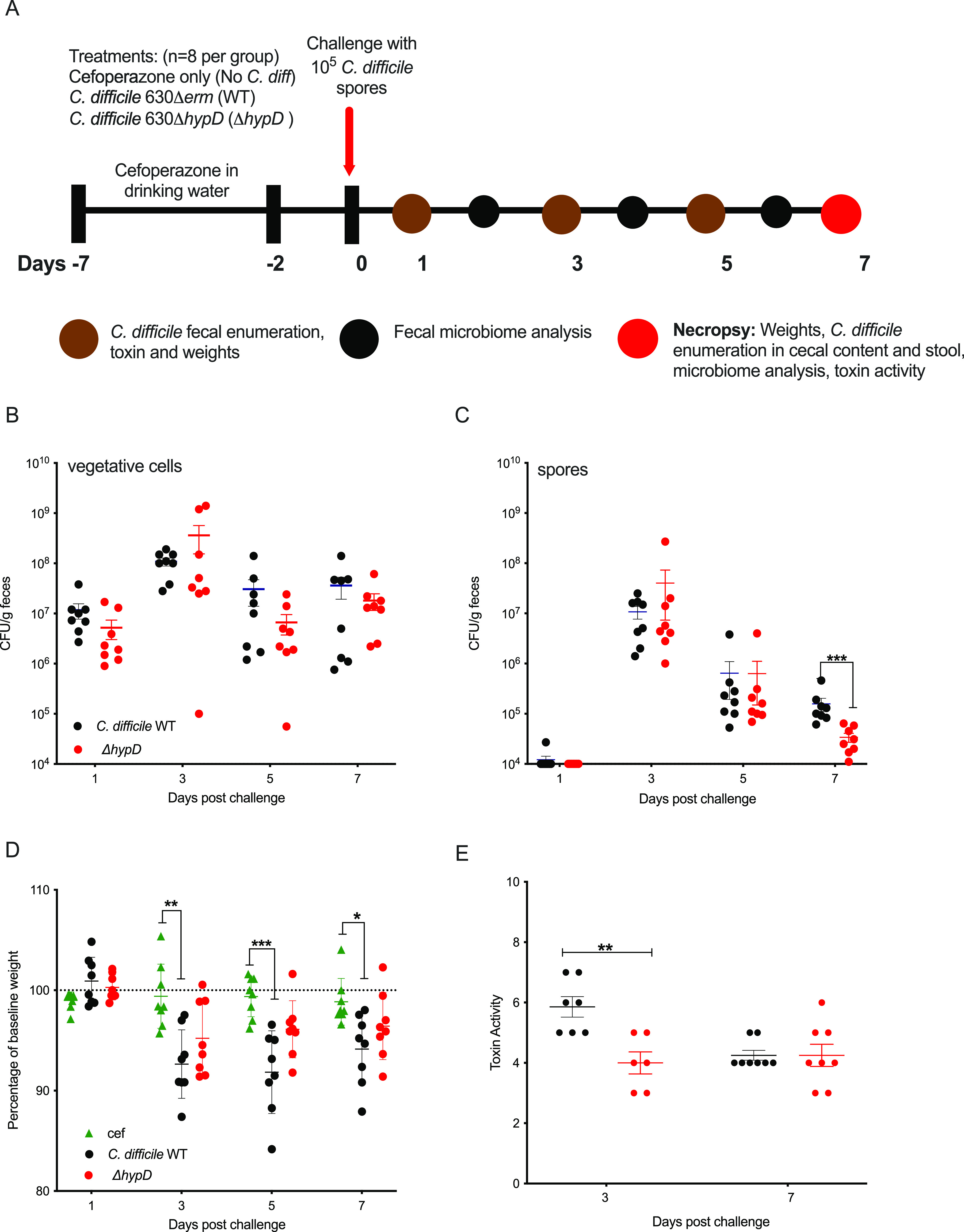
WT C. difficile induces more weight loss and toxin activity than the ΔhypD mutant in a mouse model of CDI. (A) Schematic depicting experimental design. All mice (n = 24) received the antibiotic cefoperazone in their drinking water. Subsets of mice were orally challenged with C. difficile 630Δerm (WT, n = 8) or C. difficile 630ΔhypDΔerm (ΔhypD, n = 8). The third group of mice were only treated with cefoperazone (no C. diff, n = 8). (B–C) C. difficile vegetative cell (B) or spore (C) CFU in feces on days 1, 3, 5, and 7 postchallenge. (D) Mouse weights from 1, 3, 5, and 7 days postchallenge, shown as a percentage of baseline weight for each mouse from day 0. (E) Toxin activity on 3 and 7 days postchallenge. Statistical significance for data shown in B–E was determined using Mann-Whitney (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001).
