FIG 1.
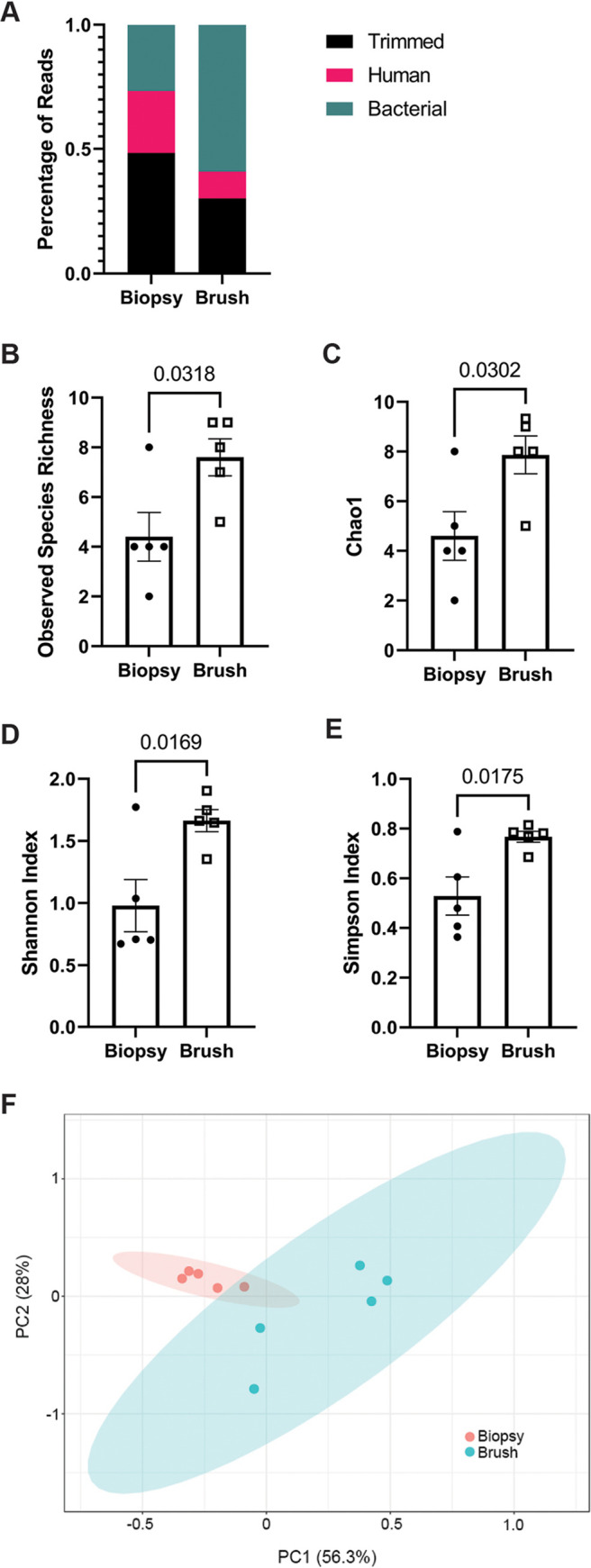
Cytology brush sampling compared to biopsy samples results in higher abundance of bacteria-derived sequence reads and increased diversity. Metatranscriptomic analysis of bacterial communities was performed on paired cytology brush samples and colon pinch biopsy samples from five healthy participants undergoing colonoscopy. (A) Percentage of sequencing reads broken down in terms of bacterial, human, and trimmed reads between sample types. (B to E) Alpha diversity calculated in MicrobiomeAnalyst using the methods of observed species richness (B), Chao1 (C), Shannon (D), and Simpson (E). Values for each subject are shown as a symbol, and bars represent the group means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Noted P values were determined by unpaired Student’s t test. (F) Beta diversity was calculated by the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity index and shown by PCoA.
