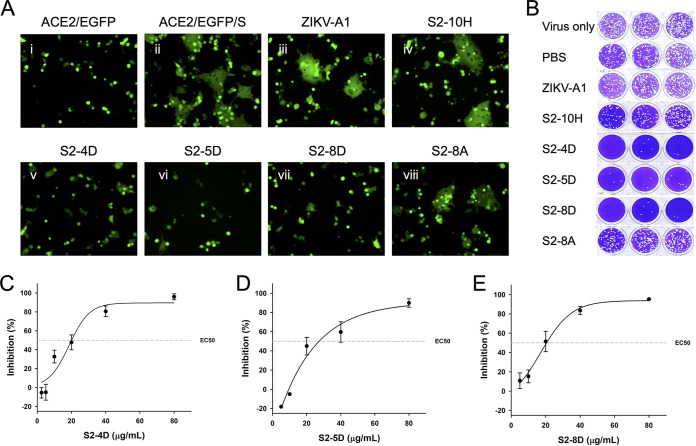
FIG 2.
The functionality of anti-S2 mAbs on inhibition of membrane fusion and virus infection. (A) For performing the S protein-mediated syncytium formation assay, ZIKV-A1 (isotype control antibody), S2-10H, S2-4D, S2-5D, S2-8D, or S2-8A (100 μg/mL for each) was preincubated with S protein-transfected 293T cells individually, before being added to the EGFP-transfected ACE2-293T cells. After 16 h of coculture, the syncytium formation was observed by fluorescence microscopy. (B) For performing the three biological replicates (n = 3) of plaque reduction assay, the indicated antibody (100 μg/mL) was incubated with the SARS-CoV-2 wild-type strain in the presence of 8 μg/mL TPCK-trypsin of DMEM for 1 h at 37°C. Antibody-virus mixtures (200 μL/well) were subsequently added to the Vero E6 cell monolayers for one additional hour in 24-well plates. Five to 7 days later, cells were fixed with formaldehyde and stained with crystal violet. (C–E) The 50% of neutralization (EC50) of SARS-CoV-2 infection by mAbs S2-4D, S2-5D, and S2-8D were determined by using a series of diluted MAb solutions (80, 40, 20, 10, 5 μg/mL) in the plaque reduction assay. Data are presented as means ± SD of three biological replicates (n =3), and further graphed by linear regression.