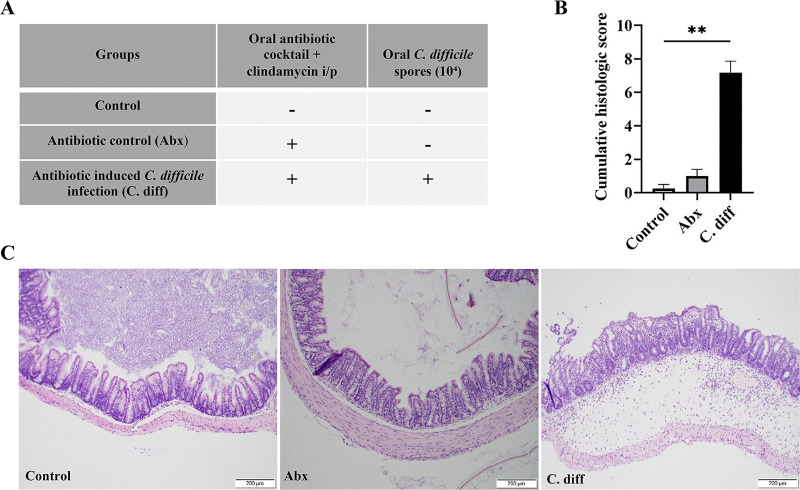
FIG 1.
Alterations in the gut mucosa in antibiotic-induced and C. difficile infected mice. (A) Experimental outline: Three-4 weeks old C57BL/6 mice (n = 18/group) are treated with an oral antibiotic cocktail or PBS and an intraperitoneal clindamycin injection or PBS to induce gut dysbiosis and then challenged with 104 C. difficile spores or PBS. The serum, cecal contents, and tissues were collected 2 days postinfection (n = 18). (B) Histopathology of the colon from different treatment groups: colonic mucosa of the C. diff group exhibited severe epithelial damage, mucosal edema, and neutrophil infiltration compared to controls. (C) Cumulative histologic scores (0–9 scale): C. difficile infection induces severe colitis in mice (n = 8). All data (C) are presented as the mean, and error bars indicate SEM. One-way ANOVA with adjusted P-value was used to test for statistical significance **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.