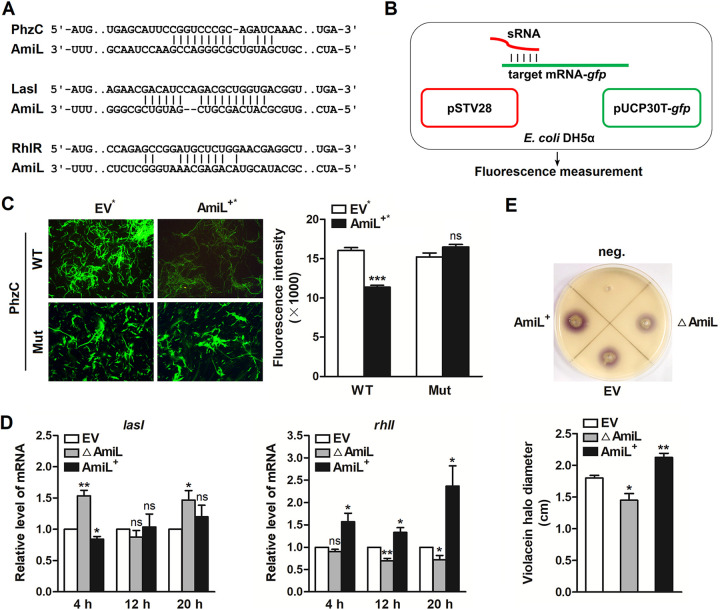
FIG 6.
AmiL directly targeted PhzC, and showed significant regulations of the las and rhl systems. (A) AmiL and its putative binding sequence in the CDS of PhzC, LasI, and RhlR. (B) A green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter system was constructed to investigate the direct interactions between sRNA and its potential targets. (C) The plasmid pSTV28 (EV*) or pSTV28-amiL (AmiL+*) was co-transformed with a GFP reporter plasmid (pUCP30T-gfp) containing a wild-type (WT) or mutant (Mut) sequences of PhzC mRNA into E. coli DH5α, then the fluorescence was measured by microscopy, and the intensity was detected by a BioTek Synergy H1 microplate reader and expressed in AU as F485/535. (D) PAO1 carrying the pROp200 EV or pROp200-amiL (AmiL+), and amiL-deleted PAO1 carrying pROp200 (△AmiL) were cultured in LB for 4 h, 12 h, and 20 h, respectively, then the expression levels of lasI (left) and rhlI (right) were measured by qRT-PCR. (E) The EV, △AmiL, and AmiL+ strains were added into the well of LB agar plates containing C. violaceum CV026 and incubated at 30°C for 24 h, the violacein halo production was observed (top) and the diameter of the halo was measured (bottom). Data are shown as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, non-significant.