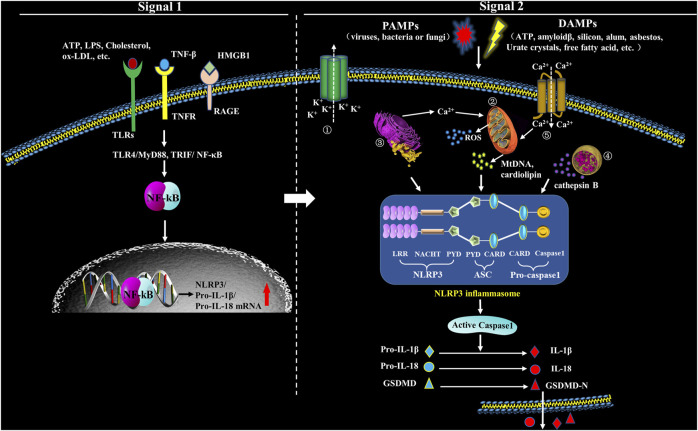
FIGURE 1.
Formation and structure of NLRP3 inflammasome. Upon exposure to PAMPs or DAMPs, TLRs will be phosphorylated, which will subsequently promote translocation of NF-κB into the nucleus and activate it, which has an action to promote the transcription of NLRP3, leading to expression of pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 that locate in the cytoplasm before maturation. Therefore, the signals in this step (Signal 1) are priming. The second step signals (Signal 2) are triggering and have an action to activate the inflammasome via promoting oligomerization of NLRP3, ASC and procaspase-1. The complex formation of NLRP3 inflammasome, then, catalyzes the conversion of pro-caspase-1 to caspase-1, which cleaves pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18, and subsequently cuases extracellular secretion of IL-1β and IL-18. In the second step, five models have been introduced to explicate inflammasome activation: ① Multiple signal transduction pathways triggered by PAMPs/DAMPs all depending on K+ efflux, which subsequently cause the interaction among different NLRP3-NEK (NIMA related kinase) and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. ② PAMPs and DAMPs trigger the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), impair mitochondria, and cause autophagic dysfunction which resut in the assembly of NLRP3 inflammasome and activate the inflammasome complex. ③ Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress activates NLRP3 inflammasome through various factors, including UPR, ROS production, calcium homeostasis and/or lipid metabolism. ④ Uptake of crystalline or other ligands such as monosodium urate (MSU), amyloid-β and silica causes lysosomal rupture and leakage of lysosomal contents like cathepsin B, thus resulting in the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. ⑤ Agonists of NLRP3 induce Ca2+ from extracellular milieu and from ER Ca2+ stores release to cytoplasm, resulting in cytosolic Ca2+ increase. The overload of mitochondrial Ca2+ would cause mitochondrial ROS production, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage and release of mitochondrial contents, which in turn triggers the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome.