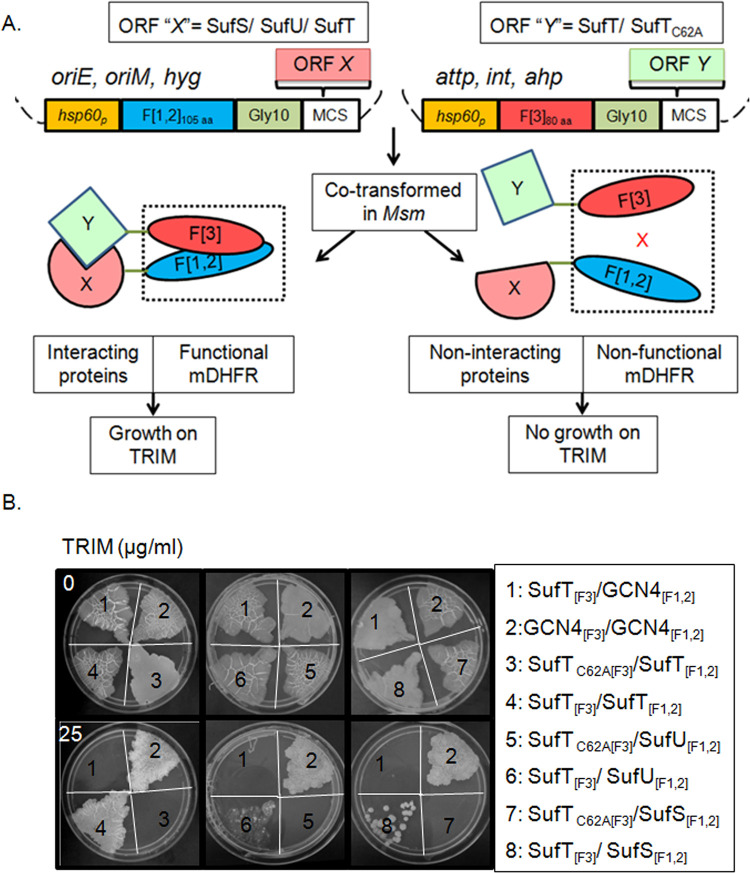
Fig 2. SufT interacts with SufS and SufU of SUF system.
(A) Model illustrating the principle of M-PFC. Two independent plasmid constructs for candidate proteins X and Y are shown in fusion to complementary mDHFR fragments F [1, 2] and F [3], respectively. Co-transformation of XF [1, 2] and YF [3] fusions in Msm results in the functional reconstitution of mDHFR activity and subsequent growth on TRIM (0 and 25 μg/mL; concentration) plates, whereas proteins that do not interact will not reconstitute F [1, 2] and F [3] and consequently no growth on TRIM plates. Components of vectors, aph confers resistance to KAN; hyg confers resistance to HYG; hsp60p is the hsp60 promoter; oriM is the origin of replication for propagation in mycobacteria; oriE is the origin of replication for propagation in E. coli; and int and attP are the integrase and phage attachment sites, respectively, from mycobacteriophage L5. (B) M-PFC based demonstration of C62 dependent specific protein-protein interaction of SufT with SufT, SufU and SufS. Msm as a host was co-transformed with plasmid construct expressing 1) SufT[F3]/GCN4[F1,2] (negative control), 2) GCN4[F1,2]/GCN4[F3] (positive control), 3) SufTC62A[F3]/SufT[F1,2], 4) SufT[F3]/SufT[F1,2], 5) SufTC62A[F3]/SufU[F1,2], 6) SufT[F3]/SufU[F1,2], 7) SufTC62A[F3]/SufS[F1,2] and 8) SufT[F3]/SufS[F1,2]. M-PFC experiments were repeated thrice, one representative image is shown here.