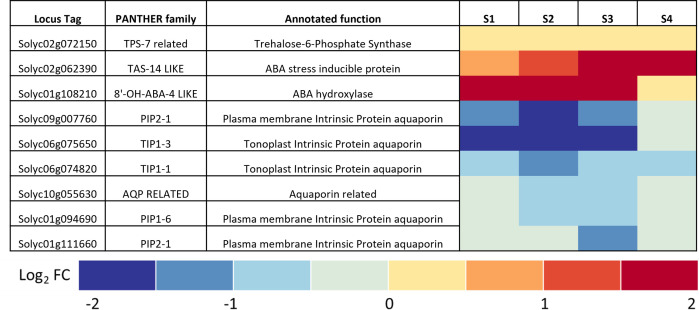
Fig 1. R. solanacearum infection consistently changes expression of nine tomato genes involved in trehalose metabolism and water stress physiology.
Meta-analysis of transcriptomic data from four different experiments measuring gene expression of tomato plants responding to infection by R. solanacearum identified nine genes of interest that were commonly differentially expressed across all data sets. The heatmaps show relative expression (as log2 fold change) compared to mock-inoculated control plants of all tomato genes that were both: 1) Annotated with the terms trehalose, drought, or abscisic acid / ABA; and 2) Identified by the meta-transcriptomic analysis as significantly differentially expressed across four different tomato RNAseq studies. The four studies were: S1, roots of wilt-susceptible West Virginia 700 tomato plants (WV) sampled 24 h after infection with R. solanacearum strain K60; S2, roots of WV sampled 48 h after infection with R. solanacearum strain K60; S3, seedling roots of wilt-susceptible cv. Bonny Best (BB) sampled 24 h after infection with R. solanacearum strain GMI1000; S4, mid-stems of BB sampled 72 h after inoculation with R. solanacearum strain GMI1000. Tomato locus tags, gene names, and PANTHER families are from NCBI and the Sol Genomics Network, accessed in 03/2020. Transcriptomic data were normalized across experiments to allow comparisons as described in Methods.