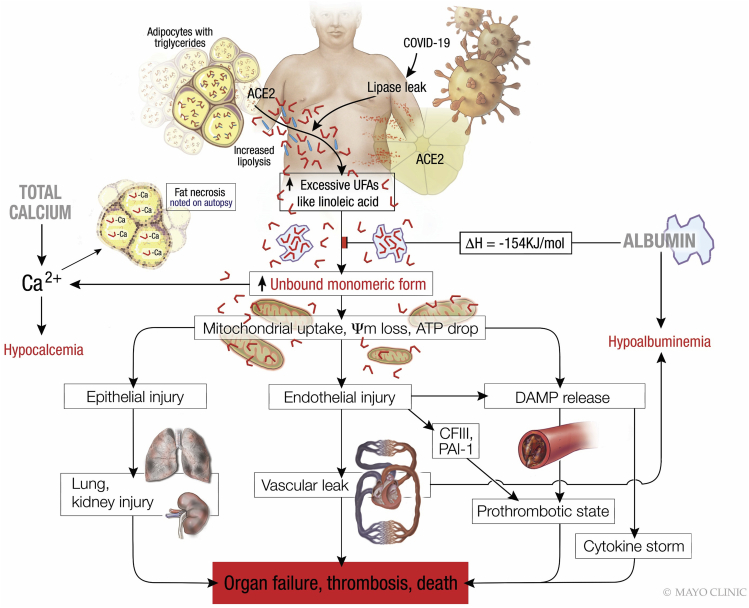
Figure 8.
Schematic describing the pathophysiology observed in severe COVID-19, wherein lipolytically generated LA results in the organ failure, thrombosis and death preceded by hypocalcemia and hypoalbuminemia
The red L shaped structures denote unsaturated fatty acids like LA, which are present in excess although the blue straight lines denote saturated fatty acids. When the amount of unsaturated fatty acids like LA exceeds the ability of albumin to bind them, the unbound LA reacts with calcium causing hypocalcemia. Excess unbound LA is taken up by cells, causing mitochondrial depolarization, and consequent epithelial and endothelial injury with DAMP release, the latter among which causes the cytokine storm. The endothelial injury causes vascular leak, and hypoalbuminemia in addition to the release of procoagulant coagulation factor III (CFIII) from basement membranes, which with DAMPs promote thrombosis. These plus plasminogen activation inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) result in a prothrombotic state and worsening organ failure which can result in death.