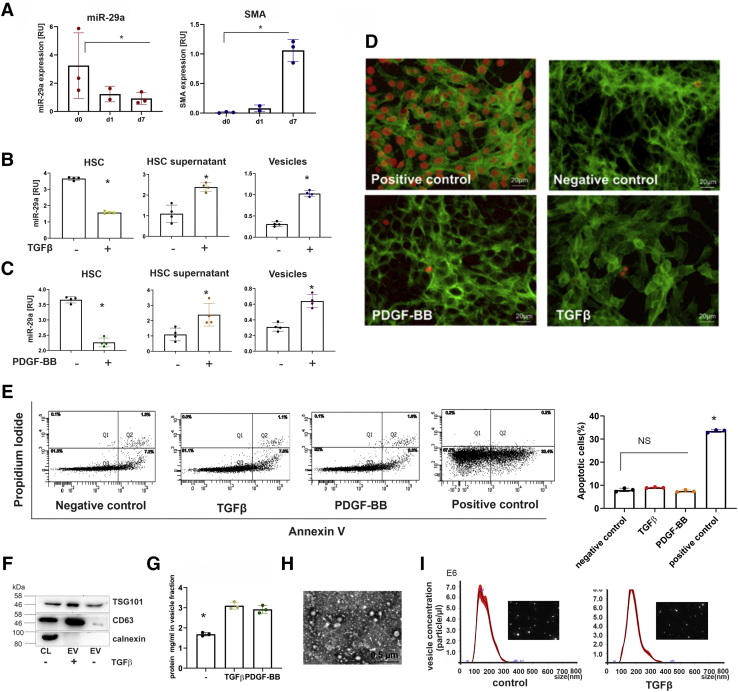
Figure 1.
Intracellular and extracellular miR-29a levels of HSC in response to stimulation with TGFβ or PDGF-BB. MicroRNA-29a levels and αSMA expression freshly isolated HSC (d0) in comparison with levels in HSC of early (day 1, d1) and late primary culture (day 7, d7). Expression profiles were determined in triplicates by quantitative PCR from 3 independent primary HSC preparations (A). In response to TGFβ (B) or PDGF-BB (C) treatment, cellular miR-29a in immortalized HSC (HSC-T6) and extracellular miR-29a in HSC culture supernatants as well as in vesicles were quantified by real-time PCR (B and C). After stimulation by TGFβ and PDGF-BB, apoptosis was determined by TUNEL analysis in HSC; DNase-treated HSCs were used as positive control. HSC were counterstained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated phalloidin. TUNEL-positive cells are shown by red fluorescence (D). HSCs were stained with annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide and analyzed by flow cytometry (E). The percentages of apoptotic cells after TGFβ, PDGF-BB, or H2O2 (positive control) treatment are shown. (∗P value <.05) (E). Vesicular fractions from supernatants of TGFβ- or PDGF-BB-stimulated HSC were characterized by immunoblotting using antibodies against EV markers, TSG101 and CD63. Calnexin was used as control for intracellular component (F). The amounts of secreted vesicles released from control HSC or TGFβ or PDGF-BB treated HSC were estimated by protein determination of the respective extracellular vesicular fractions (G). Moreover, isolated vesicles were imaged by electron microscopy (H) and the nanoparticle tracking method (I).