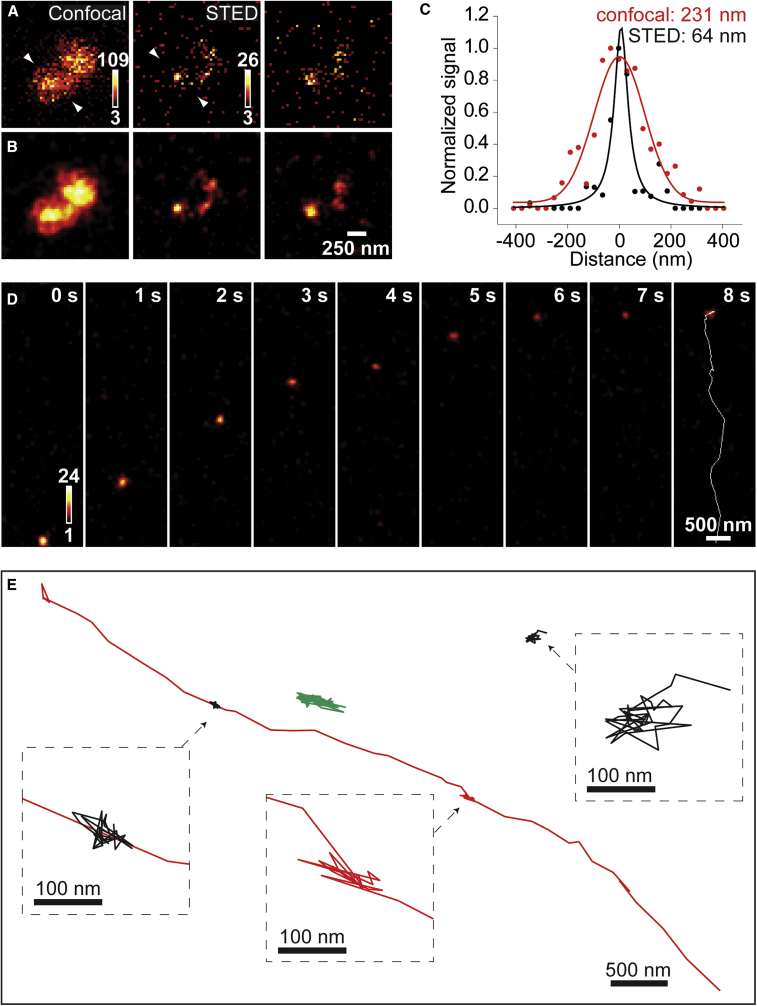
Figure 4.
STED microscopy of synaptic vesicles labeled with C2-ATTO647N
(A) Raw confocal and STED images of a small field of neurons briefly exposed to 4 μM C2-ATTO647N at 37°C. Although dim, STED-resolved spots can be clearly distinguished from random noise since they appeared in consecutive frames (middle and right column panels).
(B) Smoothing the above images with a 2D Gaussian filter with an FWHM of 80 nm better differentiates individual labeled objects in STED mode, but not in confocal mode.
(C) Intensity profiles of a stationary vesicle (measured across arrowheads in A) were fitted to either a Gaussian (confocal) or a Lorentzian function (STED) to give the indicated FWHM values.
(D) Image sequence (smoothed) from an STED movie recorded at 4.9 Hz. The white line in the last frame depicts the trajectory of the vesicle.
(E) Examples of different types of vesicle mobility in one movie. Vesicles show either directed (red) or diffusive motion (green) or remain stationary (black) throughout the whole recording. Insets show expanded views.