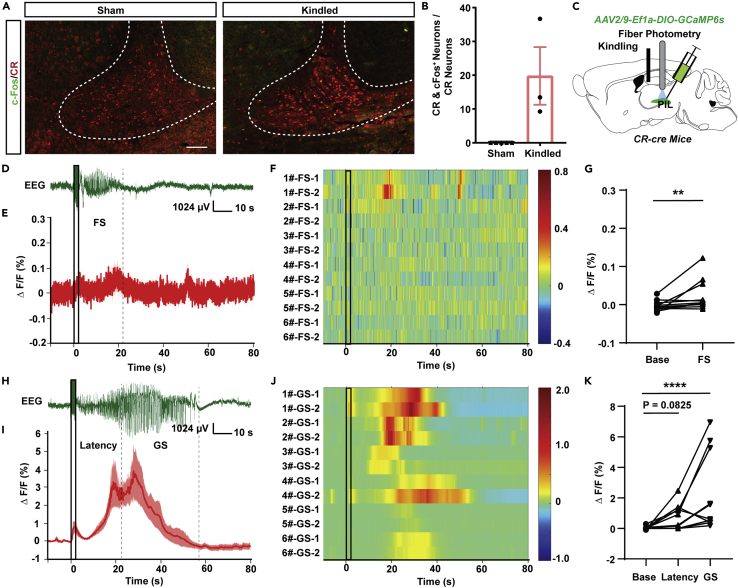
Figure 1.
CR neurons in the PIL are activated during hippocampal seizures
(A) Representative images of immunofluorescence of colocalizations (yellow) of CR (red), c-Fos (green) in the PIL region of sham and kindled mice (Scale Bar: 100 μm).
(B) Percentages of CR+ neurons expressing c-Fos in sham and kindled mice. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(C) Experimental schematic of the viral injection and photorecording of CR-GCaMP6sPIL mice. The AAV2/9-Ef1a-DIO-GCaMP6s was injected into the PIL of CR-cre mice.
(D) Representative EEG of a focal seizure (FS) in hippocampal kindling model. The black rectangles represent kindling stimulation.
(E) Fiber photometry of Ca2+ activities of PIL CR neurons during FS in PIL (n = 6 mice). Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(F) Heatmap illustration of Ca2+ signals aligned to the initiation of stimulation. Each row represents the typical calcium signal of each trial during FS (6 mice, each mouse with two trials). Color scale indicates ΔF/F and warmer colors indicate higher fluorescence signal.
(G) Group data of trials showing quantification of the average ΔF/F during Base and FS of mice. “FS” is the average ΔF/F of the seizure duration (ADD period) and “Base” is average ΔF/F during 10 s before kindling stimulation. ∗∗p < 0.01, Wilcoxon test.
(H) Representative EEG of a generalized seizure (GS) in hippocampal kindling model.
(I) Fiber photometry of Ca2+ activities of PIL CR neurons during GS in PIL (n = 6 mice). Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(J) Heatmap illustration of Ca2+ signals aligned to the initiation of stimulation. Each row represents the typical calcium signal of each trial during GSs (6 mice, each mouse with two trials). Color scale indicates ΔF/F and warmer colors indicate higher fluorescence signal.
(K) Group data of trials showing quantification of the average ΔF/F Ca2+ activity during Base, Latency to GS and GS states. ADD is separated into Latency to GS and GS according to the time mice rearing bilateral forelimbs. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, Friedman test.