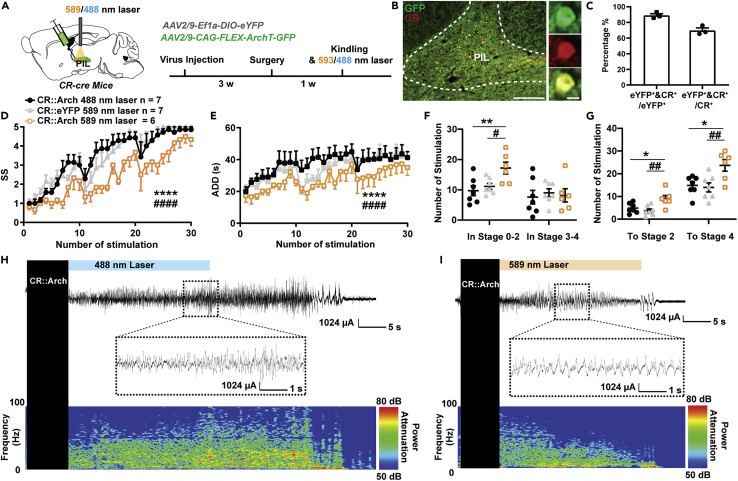
Figure 3.
Optogenetic inhibition of CR neurons in the PIL retards seizure progression
(A) Experimental schematic of viral injection and photostimulation CR-ArchPIL mice. AAV2/9-CAG-FLEX-ArchT-GFP was injected in the PIL of CR-cre mice.
(B) Representative images of the PIL from a CR-ArchPIL mouse, showing the overlap of GFP and CR neurons (red). Scale Bar: 200 μm. Right, scaled up immunoreactivity image of GFP, CR, and colocalization of both stains (yellow). Scale bar: 20 μm.
(C) Quantification of the percentage of GFP neurons that co-express CR (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(D–G) Effects of optogenetic inhibition of PIL CR neurons on developmental seizure stage (SS, D), after-discharge duration (ADD, E), number of stimulations in different seizure stage (F), number of stimulations to different seizure stage (G). The number of mice in each group is indicated in figure. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, compared with CR::Arch 488 nm laser group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ####p < 0.0001, compared with CR::eYFP 589 nm laser group; For D, E, two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test; For F and G, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(H and I) Representative EEGs and corresponding power spectra of mice.