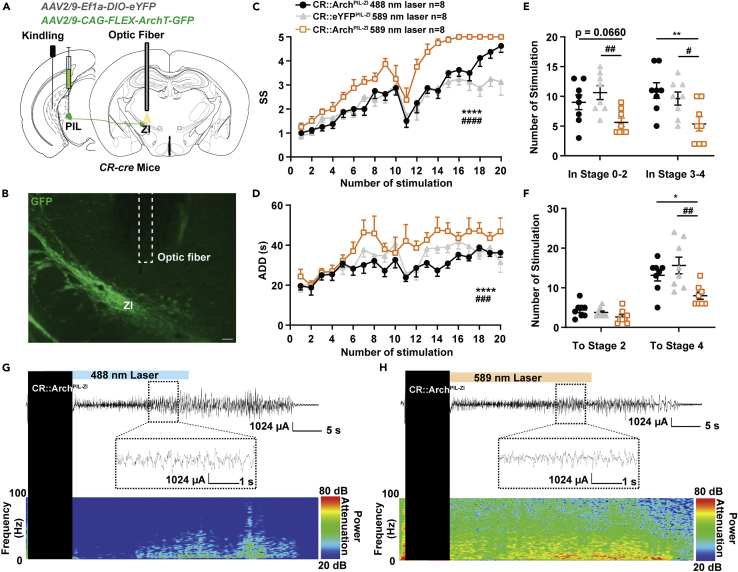
Figure 6.
Inhibition of PIL-ZI CR circuit proliferates hippocampal seizure
(A) Experimental schematic diagram optogenetic inhibition of the PIL-ZI CR projections in CR-ArchPIL mice.
(B) Representative image showing the Arch-GFP axon fibers within the ZI projected from the PIL and the optic fiber (dotted line). Scale bar: 200 μm.
(C–F) Effects of optogenetic inhibition of PIL-ZI CR projections on seizure stage (SS, C), after-discharge duration (ADD, D), the number of stimulations in seizure stages (E), and the number of stimulations needed to reach each stage (F). The number of mice in each group is indicated in figure. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, compared with CR::ArchPIL−ZI 488nm laser group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, ####p < 0.0001, compared with CR::eYFPPIL−ZI 589nm laser group; For C, D, two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test; For E, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test; For F, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(G and H) Representative EEGs and corresponding power spectra (H) of mice.