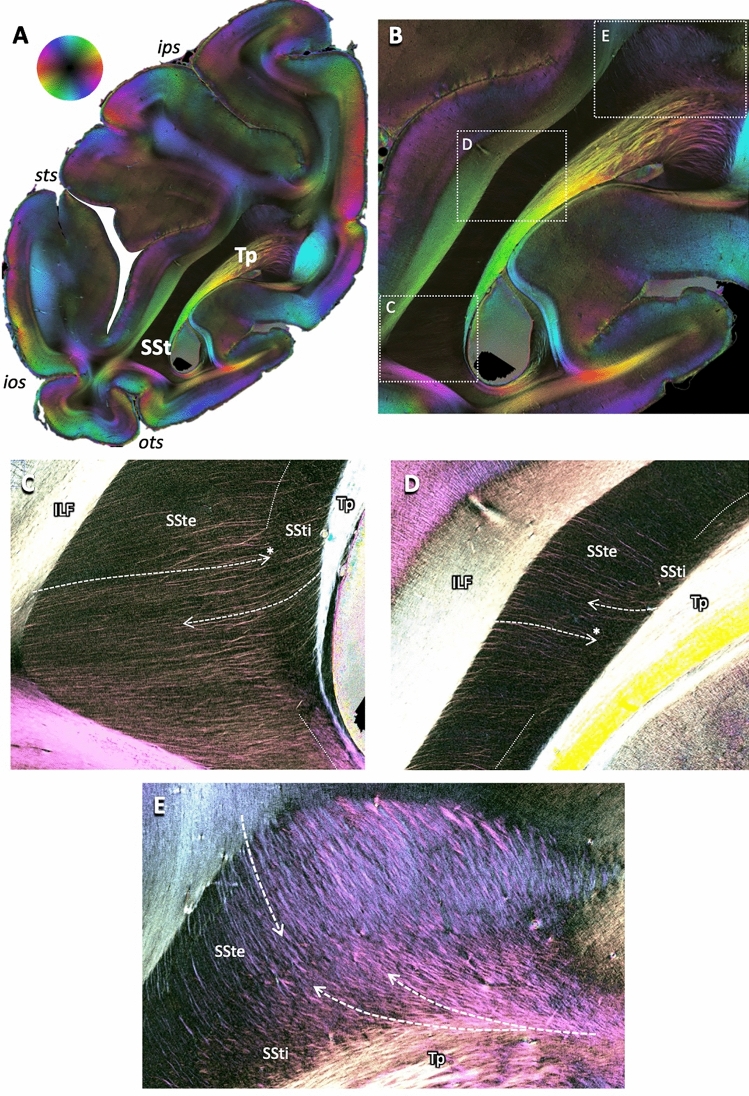
Fig. 3.
Principles of fibers crossing through or entering and leaving the sagittal stratum. A Fiber orientation map (FOM) of a coronal brain section of a vervet monkey brain (same as first section in Fig. 2). Fiber directions according to the color sphere at the top, with fading colors indicating change of fiber direction from within to out of the sectioning plane. B Enlarged view of the complete sagittal stratum. Boxes with dotted white outlines indicate regions of interest as highlighted in C–E. C–E Enlarged views of the dorsal, middle and ventral aspects of the sagittal stratum as indicated in (B), using enhanced color contrasts. Dashed arrows indicate courses of fibers leaving the tapetum (Tp) or leaving or entering the sagittal stratum laterally and dorsally to the surrounding white matter. Note that some fibers course through the external part of the sagittal stratum (SSte), but stop as they enter the internal part (SSti), indicating a change of direction from the sectioning plane to a course perpendicular to it (marked by asterisks at the heads of the arrows in D and E). For other conventions, see Fig. 2