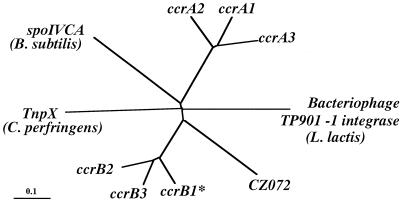
FIG. 4.
Phylogenetic relationships among ccrA genes, ccrB genes the ORF CZ072, and three site-specific recombinases. Three site-specific recombinases that showed a high similarity to ccr genes were selected to investigate phylogenetic relationships. They were the integrase (int) of bacteriophage TP901-1 found in L. lactis (1,458 bp; DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession no. X85213), the site-specific recombinase (spoIVCA) found in B. subtilis (1,503 bp; DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession no. D32216), and the transposase (tnpX) found in the conjugative transposon Tn4451 of C. perfringens (2,124 bp; DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession no. U15027). The nucleotide sequences of the ccrA genes (ccrA1, ccrA2, and ccrA3), ccrB genes (ccrB1∗, ccrB2, and ccrB3), ORF CZ072, int, spoIVCA, and tnpX were aligned by using the Pile-Up program with a GCG default scoring matrix. Phylogenetic relationships were developed with the Paupsearch program by the neighbor-joining method. The tree was visualized with Tree View software. The branch length indicates the distance, which is expressed as the number of substitutions per 100 bases.