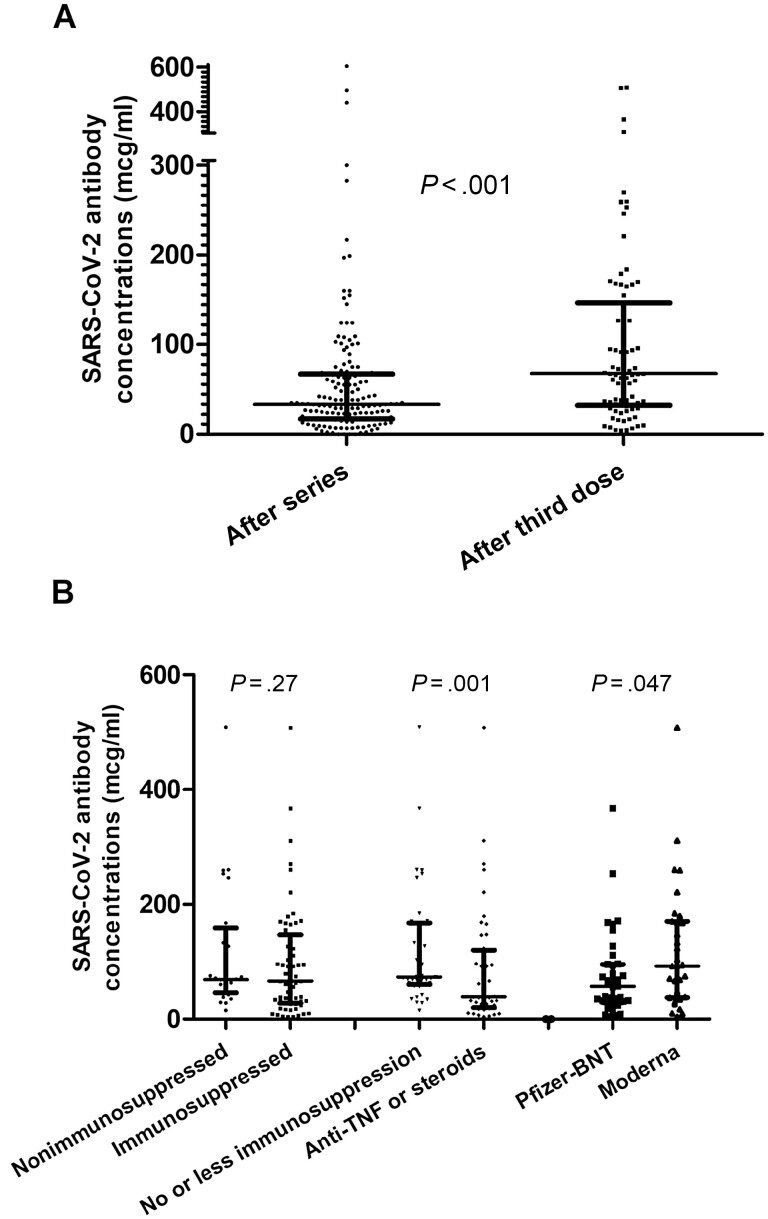
Figure 1.
A, Serum antibody concentrations in patients with IBD following the 2-dose series versus the third dose (median, 31 [IQR, 16–61] versus 68 [IQR, 32–147], respectively; P < .001). B, Left: serum antibody concentrations following the third dose in patients with IBD on nonimmunosuppressive therapy versus immunosuppressive therapy (median, 69 [IQR, 46–159] versus 66 [IQR, 28–147], respectively; P = .27). Nonimmunosuppressive therapy was defined as the absence of IBD-directed therapy or receipt of treatment with mesalamine monotherapy or vedolizumab monotherapy. Immunosuppressive therapy was defined as thiopurine monotherapy (ie, azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine), anti-TNF monotherapy, anti-TNF combination therapy (ie, plus antimetabolite), ustekinumab monotherapy or combination therapy, tofacitinib, or systemic corticosteroid therapy (ie, any of the aforementioned groups plus systemic corticosteroids). Middle: subgroup analysis with serum antibody concentrations following the third dose in patients with IBD on “no or less immunosuppression” versus anti-TNF monotherapy, anti-TNF combination therapy, and systemic corticosteroid therapy (median, 73 [IQR, 60–167] versus 39 [IQR, 20–120], respectively; P < .001). “No or less immunosuppression” was defined as the absence of IBD-directed therapy or receipt of treatment with mesalamine monotherapy, vedolizumab monotherapy, thiopurine monotherapy, or ustekinumab monotherapy or combination therapy. Tofacitinib was excluded from the subgroup analysis due to the small sample size. Right: serum antibody concentrations for patients with IBD that received 3 Moderna doses versus 3 Pfizer doses (median, 94 [IQR, 38–170] versus 62 [IQR, 31–96], respectively; P = .047). Units of serum antibody concentrations are reported as mcg/ml. Abbreviations: BNT, BioNTech; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; IQR, interquartile range; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.