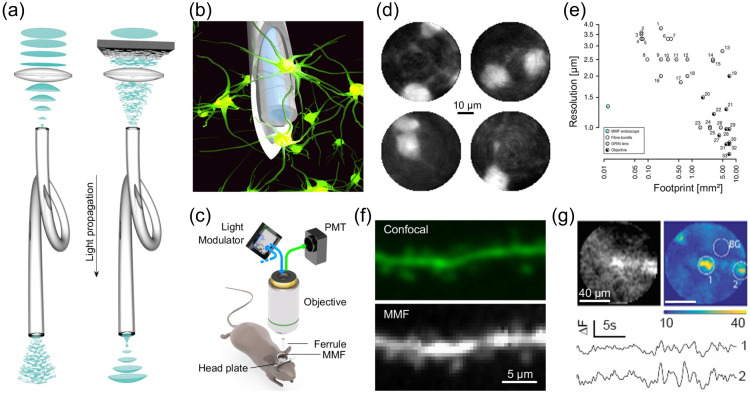
Fig. 21.
Deep brain imaging through an optical fiber. (a) Coherent light propagated through a MMF forms a speckle pattern at the output (left). Manipulation of the wavefront entering the MMF yields a desired optical field, e.g., a focal spot (right). (b)–(c) Experimental configuration for in vivo imaging. (d) Inhibitory neurons expressing tdTomato imaged in vivo (panel adapted from Ref. 403). (e) The trade-off between the fiber size and resolution. (f) Dendritic spines of a hippocampal neuron ex vivo resolved using a MMF (bottom). Comparison of the same field of view imaged with a confocal microscope (top). Panels (e) and (f) are adapted from Ref. 404. (g) In vivo neurons expressing GCaMP6f (left) and their activity visualized as standard deviation over time (right). Bottom traces show the change of signal in time after background (BG) subtraction from two regions of interest (1 and 2). Panel adapted from Ref. 405 © Optica.