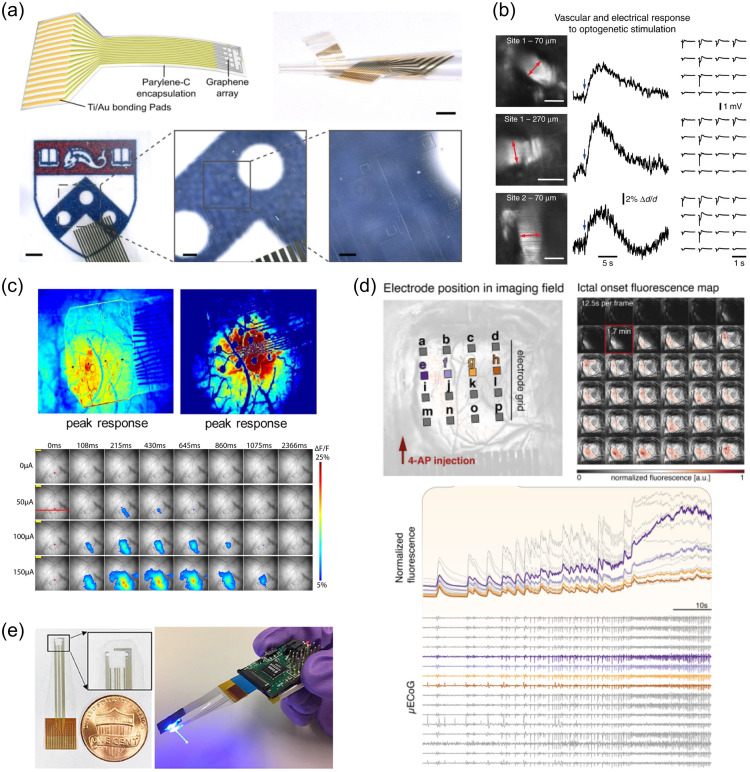
Fig. 36.
Multimodal measurements and interrogation of brain activity using transparent electrode arrays and neurophotonic technologies. (a) (Top) Design of a flexible, transparent 16-channel microECoG array for multimodal mapping the dynamics of epileptiform discharges in mouse models.663 The array is a grid of square electrodes with spacing (total recording area: 1.55 mm × 1.55 mm, total array footprint 2.75 mm × 2.75 mm. Scale bar: 2 mm). (Bottom) Photographs illustrating the optical transparency of the array in the recording area. Scale bars, left to right: 1 mm, , and . Reproduced from Ref. 663. (b) Simultaneous optogenetics, recording and hemodynamic imaging in Thy-Cr2 mice through graphene arrays.662 (Left) Line-scan imaging of arteriolar dilation induced by optogenetic stimulation under two different electrode sites (marker: FITC-dextran, red arrows show line-scan location). Scale bars: . (Middle) Average vascular diameter change and (right) light-evoked LFPs recorded at the graphene electrode sites. Reproduced from Ref. 662. (c) Maps of cortical responses to co-localized electrical stimulation delivered through graphene electrodes in GCamp6f mice.664 (Top) fluorescence intensity in response to cortical electrical stimulation under (left) a graphene and (right) a platinum array of the same size. (Bottom) Spatiotemporal maps of cortical activation following electrical stimulation at varying intensities delivered from a transparent graphene electrode (marked with the red star). Adapted from Ref. 664. (d) Multimodal analysis of ictal state transitions in acute mouse preparations induced by 4-aminopyridine (4-AP).663 (Top left) Schematics of the relative graphene contact positions and 4-AP application site. (Top right) Propagation of the ictal wavefront at seizure onset mapped with wide-field epifluorescence imaging. (Bottom) fluorescence intensity beneath each electrode and simultaneous microECoG recordings from the graphene array during seizure onset. Adapted from Ref. 663. (e) Closed-loop graphene device for artifact-free optogenetics. (Left) Photographs of the transparent graphene array and (right) the fully assembled battery-powered, closed-loop device integrating the graphene array with an optic fiber for optogenetic stimulation. Adapted from Ref. 665.