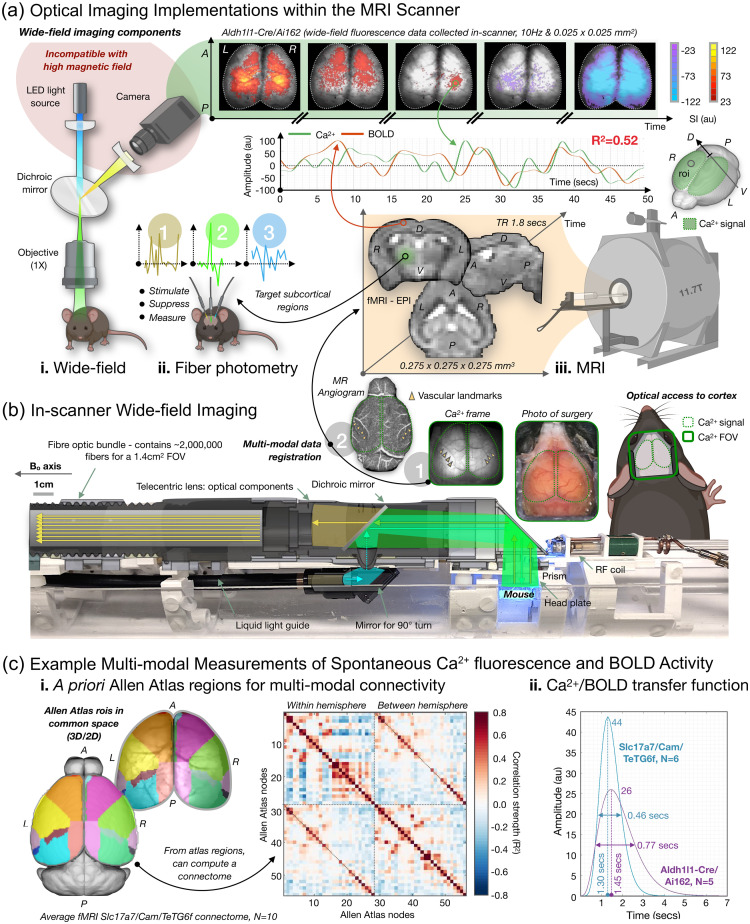
Fig. 37.
Concurrent optical imaging and fMRI. (a) Optical imaging implementations within the MRI scanner. Schematic of typical wide-field imaging components (i.). Excitation light is delivered (LED light source), passes through a dichroic mirror, and is focused onto the mouse cortex (1X objective). Emitted fluorescence signal is relayed to a camera and recorded. Example imaging frames from a movie recorded from a mouse expressing GCaMP in glia (Aldh1l1-Cre/Ai162) (top right). Data are collected in-scanner. Blooms of increased activity are in hot colors; epochs of decreased activity are in cool colors. Schematic of a typical fiber photometry experiment (ii.). Excitation light delivered and signal recorded through long fiber optic cables. Both (i.) and (ii.) can be performed within an MRI scanner (iii.) where simultaneous BOLD-fMRI data can be recorded. Wide-field imaging yields measures of cortical activity (2D images), while fiber photometry can target subcortical areas (1D time courses). Simultaneously recorded glia- (green) and BOLD (orange) spontaneous activity from a cortical roi are plotted (middle). In this example, these signals are moderately correlated (Pearson’s correlation , P < 0.05). (b) In-scanner wide-field imaging. Components and light path are indicated (image reproduced from Ref. 630). For wide-field imaging, optical access to the cortex is gained by resecting the scalp and covering the skull in dental cement, glue, and glass (right). The wide-field imaging data can be registered to the MRI data using the middle cerebral arteries as anatomical landmarks and an MR angiogram. Example multi-modal measurements of spontaneous fluorescence and BOLD activity. (c) With multi-modal data registered to a common space (i.), ROIs can be imposed (e.g., Allen Atlas regions) and a connectome computed. Multi-modal spontaneous activity can be used to compute a between contrast transfer function (ii.). Here, gamma-variant fitting630 was applied to compute a transfer function using simultaneously recorded spontaneous BOLD activity and excitatory neuronal activity (Slc17a7/Cam/TeTG6f, N = 6, plotted in blue) or glia activity (Aldh1l1-Cre/Ai162, N = 5, plotted in purple). Abbreviations: functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI, MRI, MR), light emitting diode (LED), anterior (A), posterior (P), right (R), left (L), dorsal (D), ventral (V), Pearson’s correlation (), region(s) of interest (roi, rois), signal intensity (SI), arbitrary units (au), blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD), seconds (secs), echo planar imaging (EPI), repetition time (TR), field of view (FOV), radio frequency (RF).