Fig. 3.
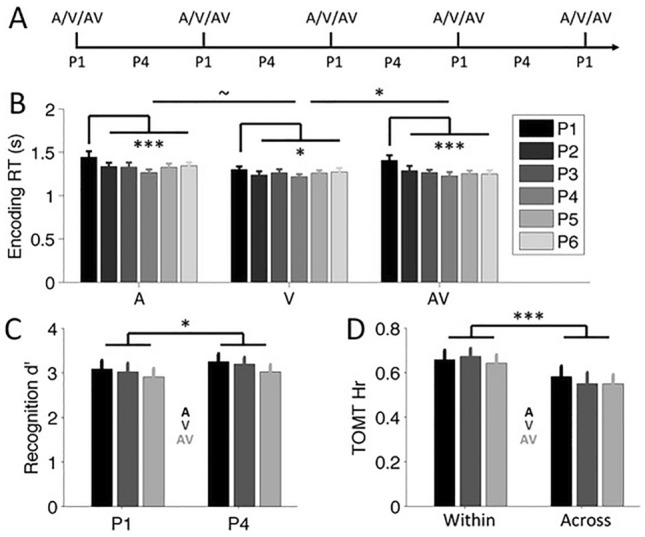
Design and results of Experiment 2. A Experiment 2 included unisensory audio (A) and visual (V) boundaries, and multisensory audiovisual (AV) boundaries. B Encoding response time (RT) for the boundary item (P1) was significantly slower than encoding time for non-boundary items at subsequent positions. Relatively slower boundary item response time was larger for AV compared to V context. C Pooled across contexts (audio in black, visual in dark gray, audiovisual in light gray), recognition sensitivity (d’) was higher for the middle non-boundary item (P4) compared to the boundary item (P1). D Pooled across contexts, temporal order memory accuracy (hit rate, Hr) for Within-context judgments was higher than for Across-context judgments. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals (Masson & Loftus, 2003). p < 0.1, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.005
