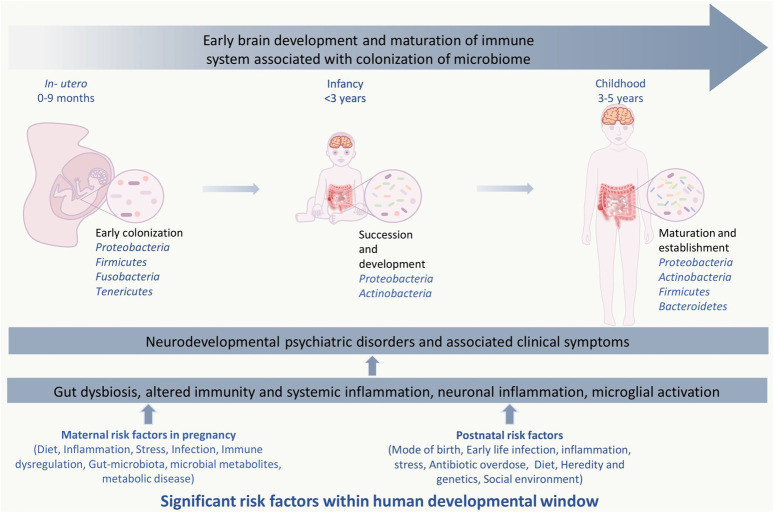
FIGURE 1.
Significant risk factors affecting events with in human developmental window could bring on neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders. The critical developmental window spans from the fetal stage until childhood, which consists of early colonization and development of the microbiome, development of the brain and nervous system, and development and maturation of the immune system. Within this period, the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome, genetics, maternal, and other reverent factors can alter the overall developmental homeostasis by causing disturbances in the immune system. Gut dysbiosis, immune alteration, and other factors induce microglial activation via inflammatory response, which leads to systemic and neuroinflammation. This negatively affects the brain development process and leads to abnormal brain development and functionality, including anxiety, depression, intellectual disability, and behavioral abnormality that can be seen in neurodevelopmental and psychotic disorders.