Figure 2.
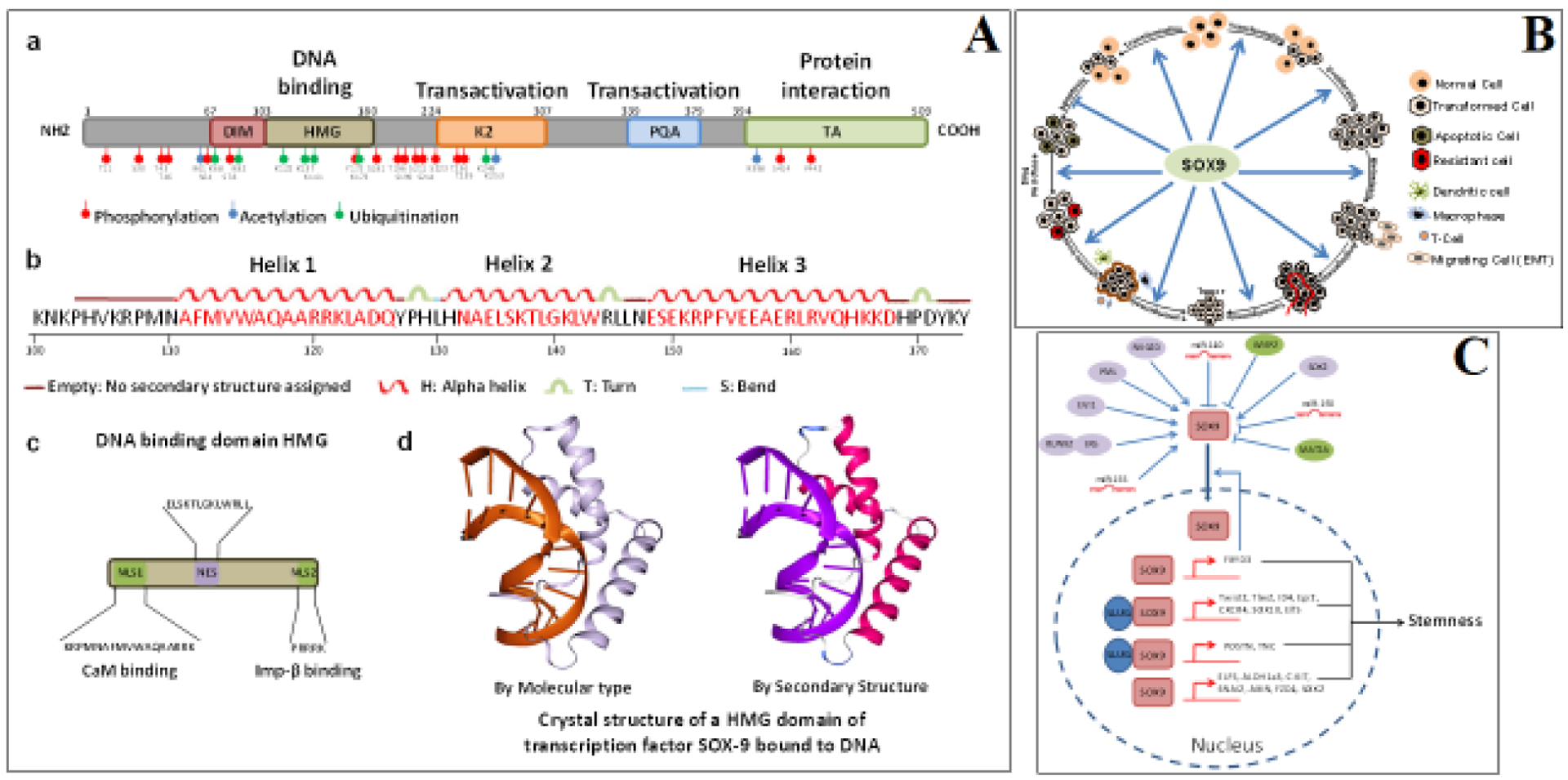
(Panel A) Schematic drawing and crystal structure of SOX9 Schematic structures of SOX9 protein. SOX9 protein has five different domains: the dimerization domain (DIM), followed by the DNA-binding high-mobility group (HMG) domain, two transactivation domains (K2 and PQA) located in a central position, and one at the C-terminal domain (TA). Post-translational modifications identified by phosphorylation sites (red), acetylation sites (blue), and ubiquitination/sumoylation sites (green) are highlighted (a). Schematic diagrams of the SOX9 DNA-binding HMG domain, showing the amino acid sequence involved in the production of its secondary helix structure (b), two independent nuclear localization signal (NLS) sequences that interact with calmodulin (CaM) and importin-β, and nuclear export signal (NES) sequences (c). Crystal structural illustrations of the SOX9 HMG domain (PDB ID: 4EUW) bound to DNA (d). (Panel B) Cellular roles of SOX9 during BC progression SOX9 plays various oncogenic roles during breast tumor initiation. SOX9 can induce cell proliferation and inhibit the expression of apoptotic pathway genes, thereby inhibiting the apoptosis of transformed cancer cells. Moreover, SOX9 induces metastatic signaling involved in progression of tumorigenesis. SOX9 contributes to tumorigenesis (both metastasis and chemoresistance) by regulating BC stem cells. Further, SOX9 contributes to tumorigenesis by promoting angiogenesis and the immune evasion of tumor cells. (Panel C) SOX9 proteins are involved in the induction of stemness of BC cells Upstream regulators and targets of SOX9 in the regulation of the stem cell properties of BC. RUNX2, RUNX family transcription factor 2; ERα, estrogen receptor alpha; EVI1, ecotropic virus integration 1 site protein; PML, promyelocytic leukemia; NKG2D, natural killer group 2D; CCN5, cellular communication network factor 5; SOX2, SRY-box transcription factor 2; MAT2A, methionine adenosyl-transferase 2A; miR-155, miR-140, miR-190. FXYD3, FXYD domain-containing ion transport regulator 3; TWIST2, twist family bHLH transcription factor 2; TBX2, T-box transcription factor 2; ID4, inhibitor of DNA binding 4, HLH protein; EGR2, early growth response 2; CXCR4, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4; SOX10, SRY-box transcription factor 10; ELF5, E74-like ETS transcription factor 5; POSTN, periostin; TNC, tenascin-C; ALDH1a3, aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member A3; cKit, KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; SNAI2 (Slug), snail family transcriptional repressor 2; AXIN, axin 1; FZD4, frizzled class receptor 4.
