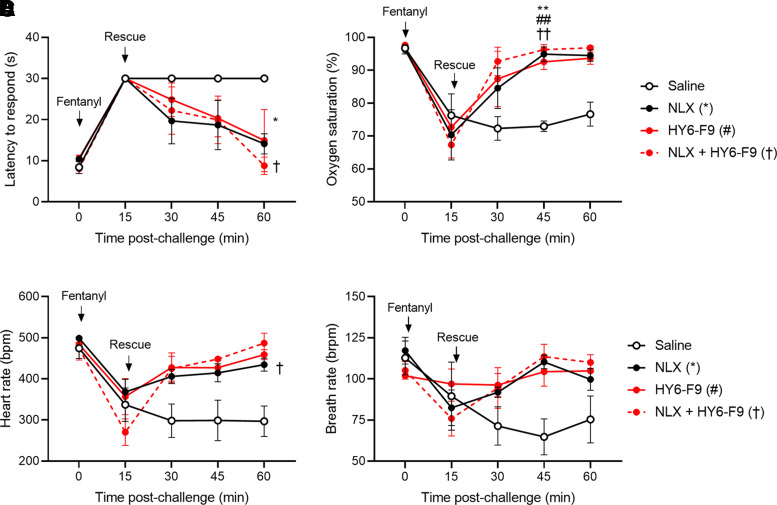
Fig. 3.
Coadministration of HY6-F9 and naloxone reverses effects of high dose fentanyl. A second cohort of naïve rats (n = 3 per group) was challenged with 0.5 mg/kg of fentanyl (s.c.) and monitored for fentanyl-induced antinociception, respiratory depression and bradycardia. Immediately following the first measurement at 15 minutes, rats were passively immunized with naloxone subcutaneously, HY6-F9 intravenously, or a combination of naloxone and monoclonal antibody intravenously. (A) Antinociception measured as latency to respond, and (B) oxygen saturation, (C) heart rate [beats per minute (bpm)], and (D) breath rate [breaths per minute (brpm)] was measured by pulse oximetry. Data are mean ± S.E.M. **p<0.01, *p<0.05 relative to saline (control).