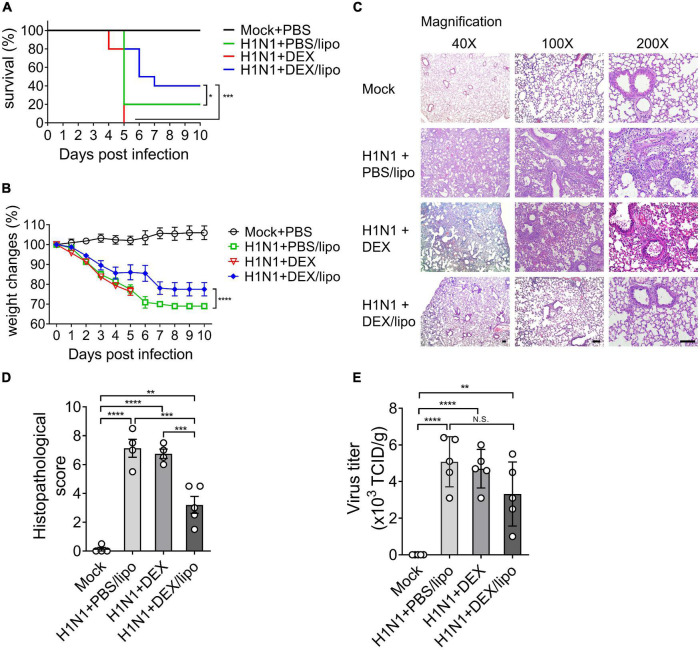
FIGURE 2.
DEX/lipo effectively reduces inflammation in mice infected with the lethal influenza A virus. Mice were infected intranasally with 105 TCID50 of influenza A virus and treated with PBS/lipo, DEX, or DEX/lipo. Mice were monitored daily to record survival rates and body weight changes. (A) Survival rate of infected mice (n = 10 per group) after PBS/lipo, DEX, or DEX/lipo treatment. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 by the log-rank test. (B) Mouse body weight change of infected mice (n = 10 per group) after PBS/lipo, DEX, or DEX/lipo treatment. ***P < 0.001 by the two-way ANOVA test. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the lungs on day 10 post-infection (n = 5 per group). Scale bar; 100 μm. (D) Comparison of the total histopathological scores of lung injury (n = 4–5 per group). Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 by the one-way ANOVA test. (E) Lung viral titers from mice on day 10 post-infection using TCID50 (n = 4–5 per group). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 the one-way ANOVA test.