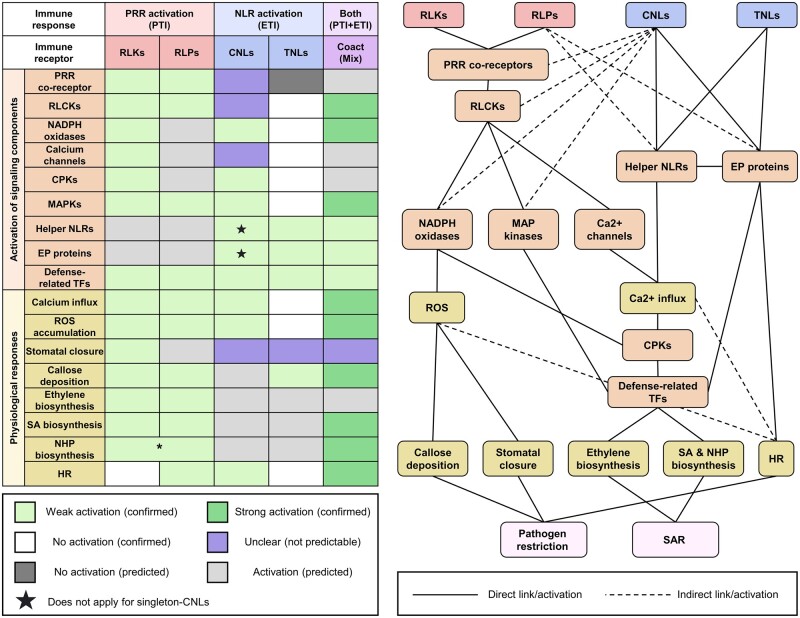
Figure 5.
Signaling components and physiological responses activated by different modes of action of immune receptors. (Left) Tabular summary of signaling components and physiological responses activated by RLKs, RLPs, CNLs, TNLs, and coactivation of PRRs and NLRs. Green (weak or strong activation) and white (no activation) shading represent confirmed responses from publications. Gray shading indicates predicted responses. Purple shading represents unclear responses that cannot be predicted. Asterisks indicate inoculation with the bacterial pathogen P. syringae pv. maculicola (Psm) leads to NHP accumulation (Wang et al., 2018c; Liu et al., 2020). (Right) PRR and NLR signaling network. Activation of PRRs (red) and NLRs (blue) lead to the activation of downstream signaling components (orange) and physiological responses (yellow), which result in resistance against pathogens (pink). Note that the activation of physiological responses can vary between immune receptors and are dependent on specific PRRs/NLRs.