Figure 6.
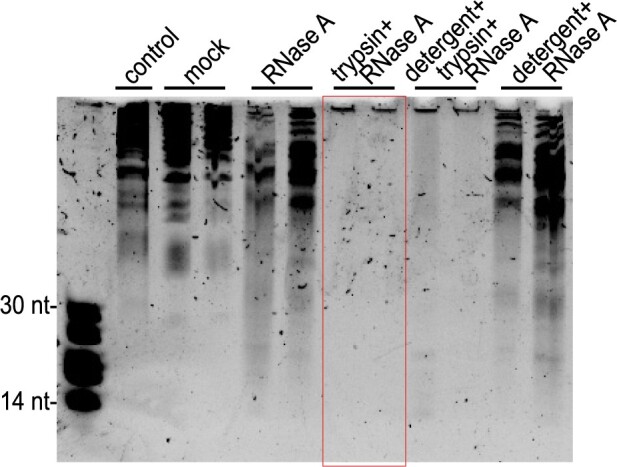
Apoplastic long RNAs are protected against RNase A digestion by proteins. P40 pellets were treated with RNase A, trypsin plus RNase A, Triton X-100 detergent plus trypsin plus RNase A, or detergent plus RNase A. The negative control was input RNA without any treatments and kept on ice. Mock was the same RNA subjected to the same incubations as the treated RNA, but without detergent, RNase A or trypsin. Following these treatments, these RNAs (and size standards, left lane) were separated in a 40% denaturing polyacrylamide gel, followed by staining with SYBR Gold nucleic acid stain. RNA size standards are shown in the left lane. The red box highlights the observation that all RNA was degraded by RNase A treatment following treatment with trypsin, even in the absence of detergent, indicating that the RNA was located outside EVs. This experiment was repeated three times on different days with different source plants and produced similar results.
