Figure 7.
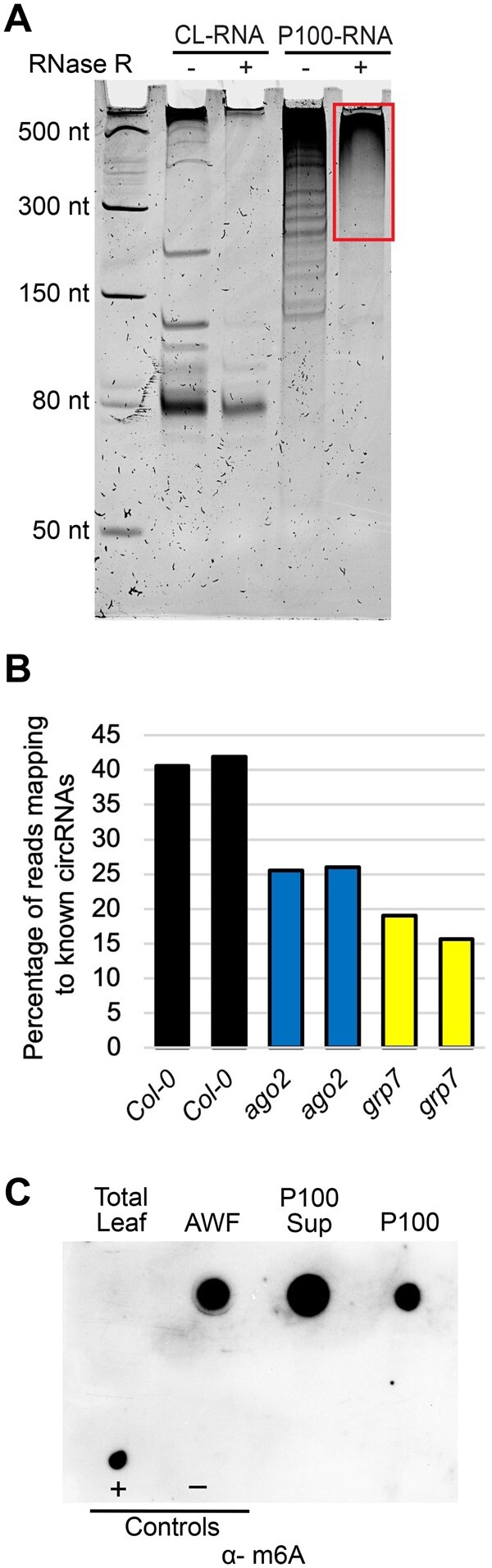
Apoplastic RNAs are enriched in circRNAs and m6A-modified RNAs. A, Apoplastic fluid contains circRNAs. Both RNAs from a P100 pellet and RNAs from total CL were purified using our P100 protocol and were then treated with RNase R, which degrades linear RNAs. These RNAs (and size standards, left lane) were then separated in a 15% denaturing polyacrylamide gel, followed by staining with SYBR Gold nucleic acid stain. Red box indicates RNase R-resistant RNA. B, Apoplastic RNA contains diverse circRNAs. P100 RNAs were treated with RNase R to remove linear RNA and then analyzed by RNA-seq using an Illumina NextSeq platform. Graphs indicate the percentage of reads that mapped to known Arabidopsis circRNAs for RNA isolated from wild-type, ago2 mutant, and grp7 mutant Arabidopsis plants. Data from two biological replicates (independently isolated P100 pellets) are shown for each genotype. C, Apoplastic RNAs are enriched in m6A modification. An aliquot of 200 ng of each of the indicated RNAs used in Figure 5 were dot blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane and then probed with an anti-m6A antibody. For positive and negative controls, 600 ng of synthetic 21-nt RNAs with identical sequences (except for a single m6A modification on the positive control) were used.
