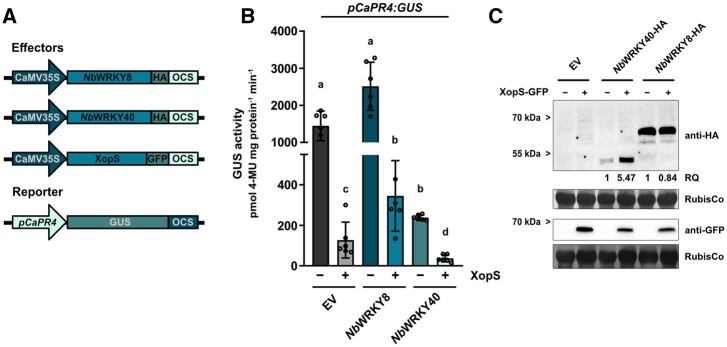
Figure 11.
XopS and WRKY40 repress expression from the CaPR4 promoter. A, Schematic diagrams of the effector and reporter constructs. The effector plasmids contain the WRKY TFs or XopS fused to the constitutive CaMV35S promoter and carry either a C-terminal HA-tag or a GFP-tag. The GUS reporter construct contains the 2 kb region upstream of the predicted translational start site of the CaPR4 gene. OCS, terminator of the octopine synthase. B, Transactivation of the pCaPR4:GUS reporter by the TFs NbWRKY8 or NbWRKY40 either in presence (+) or absence (−) of XopS. Samples were taken 24 h after Agrobacterium-infiltration of indicated effector constructs and GUS activity is expressed in pmol 4-Methylumbelliferone mg protein−1 min−1. Bars represent the mean of n = 6 biological replicates ± sd. Letters over bars represent statistical significance determined by one-way ANOVA (P < 0.05).The experiment was carried out three times with similar results. C, Verification of effector protein expression in pCaPR4:GUS reporter gene analyses. Total protein extracts from Agrobacterium-infiltrated leaves were prepared 24 hpi and protein expression was detected by immunoblotting using an anti-HA or anti-GFP antibody. The RQ of indicated proteins was determined using the Quantity Tool within the BioRad Image Lab software. Amido black staining of RubisCo served as loading control. Leaf discs from the six biological replicates used for pCaPR4:GUS reporter gene analyses were pooled for the immunoblot analysis shown here.