Figure 8.
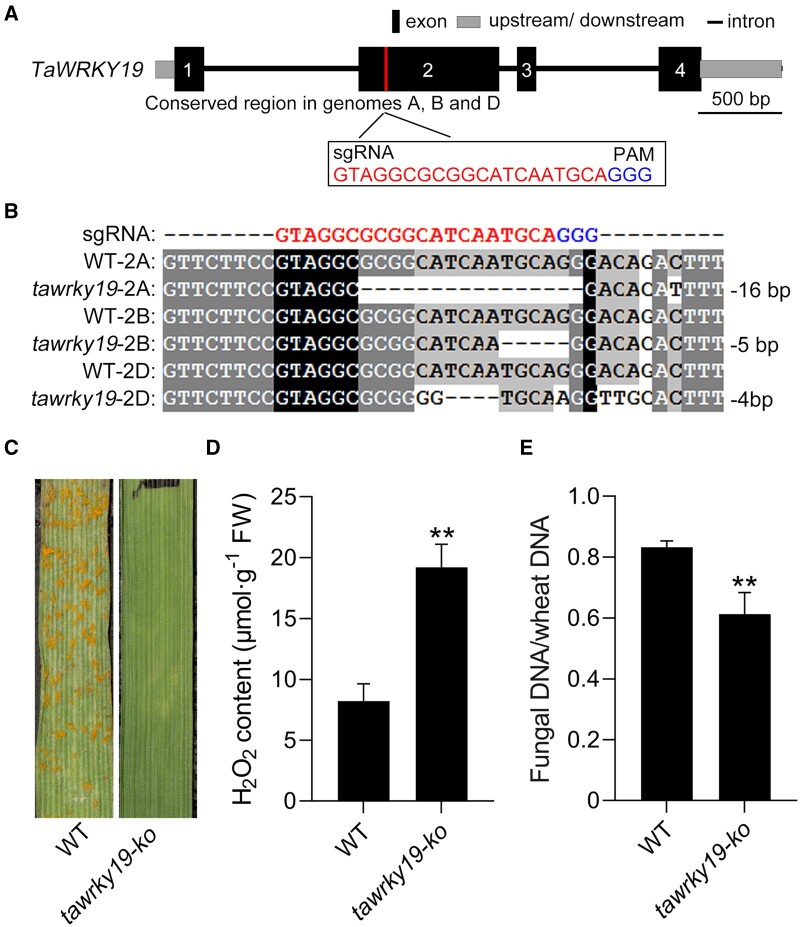
Loss of TaWRKY19 confers resistance to Pst. A, Schematic diagram of TaWRKY19 gene structure and the sequences of the two sgRNAs designed to target the three homoeoalleles (A, B, D) of TaWRKY19 for editing by CRISPR–Cas9. Black rectangles, exons. Blue letters, PAM. B, Sequences of the WT TaWRKY19 and TaWRKY19-ko (tawrky19-ko) plant at the sites targeted by the sgRNAs. The tawrky19-ko contains mutations in tawrky19-2A (16-bp deletion), tawrky19-2B (5-bp deletion), and tawrky19-2D (4-bp deletion). C, The tawrky19-ko line and the WT KN199 variety were inoculated with Pst race CYR33, and their disease phenotypes were observed at 14 dpi. D, Extracellular H2O2 contents in tawrky19-ko and WT at 24 hpi with Pst CYR33. Data are shown as means ± SD from three biological replicates. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test. **P < 0.01. E, Fungal biomass in tawrky19-ko and WT at 14 dpi with Pst CYR33, as estimated by qPCR of PsEF1 and wheat TaEF1α DNAs in infected samples and calculated with reference to gene-specific standard curves. Data are shown as means ± SD from three biological replicates. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test. **P < 0.01.