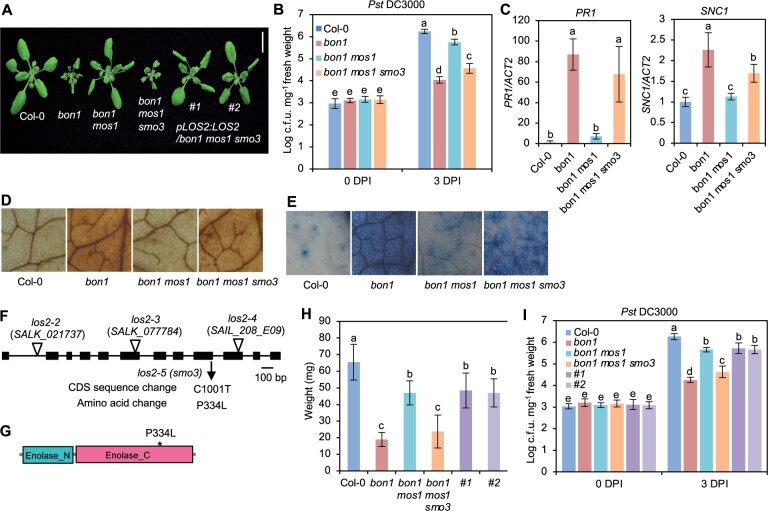
Figure 1.
A mutation in LOS2 constitutively activates immune responses. A, Morphology of Col-0 WT, bon1, bon1 mos1, bon1 mos1 smo3/los2 and two representative complementation lines of pLOS:LOS2 in bon1 mos1 smo3 (#1 and #2). Scale bar = 1 cm. B–E, Growth of bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst) DC3000 (B), analysis of PR1 and SNC1 gene expression (C), DAB staining (D), and trypan blue staining (E) in Col-0, bon1, bon1 mos1, and bon1 mos1 smo3/los2. F, Position of the point mutation generated from the ethylmethylsulfonate screen and T-DNA insertion mutations in LOS2. The position of T-DNA insertions was adapted from Eremina et al. (2015). G, Predicted functional domains of LOS2 protein by SMART. * indicates smo3/los2-5 mutation. H and I, Quantification of weight (H) and growth of bacterial pathogen Pst DC3000 (I) in Col-0, bon1, bon1 mos1, bon1 mos1 smo3, complementation lines #1 and #2. N ≥ 23 for (H). Six biological replicates were performed for (B) and (I). Three biological replicates were performed for (C). Error bars represent standard deviation (sd). Different letters indicate significant difference tested by one-way ANOVA/Duncan’s multiple range test via R 3.6.3 with “agricolae” package, P < 0.05.