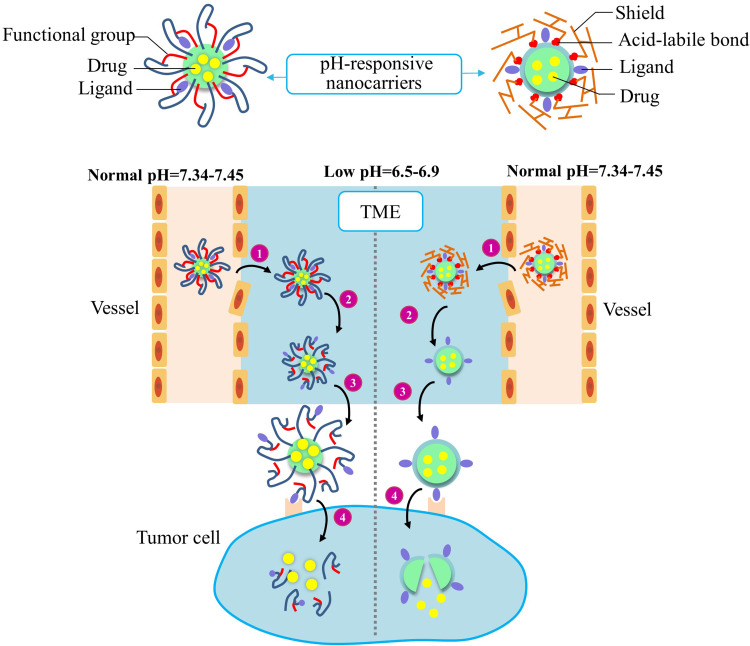
Figure 3.
Improved drug delivery efficiency by two types of acidic TME-responsive nanocarriers. The ligands of acidic TME-responsive nanocarriers are covered by either functional groups (Left) or shields (right) before reaching tumor tissues. A nanocarrier covered with functional groups will respond to the low pH by protonation/ionization of the functional groups to reveal the targeting ligands. A nanocarrier covered with shielding molecules will respond to the low pH by degradation/cleavage of the shielding molecules to present the targeting ligands. The two types of nanocarriers undergo these common steps: 1) The EPR effect-promoted penetration and accumulation of nanocarriers in tumor. 2) The low-pH TME-triggered exposure of the targeting ligands. 3) Ligands binding to the cell surface receptors. 4) Internalization of nanocarriers and drug release in cellular compartments.
Abbreviations: TME, tumor microenvironment; EPR, enhanced permeability and retention.