Figure 1.
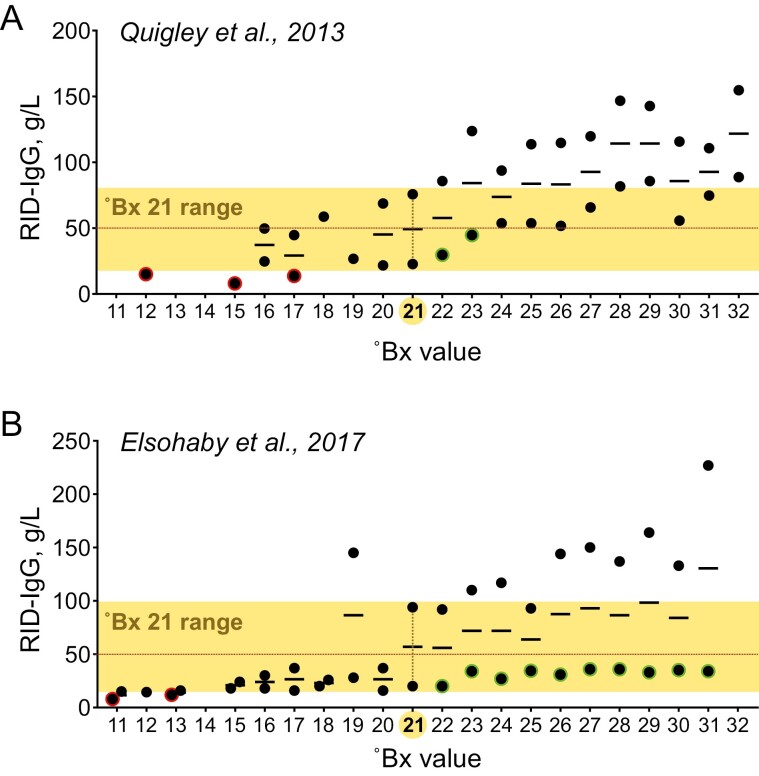
Prediction of IgG concentrations from ˚Bx values is ambiguous and inconsistent between studies. When we examine two studies correlating ˚Bx values and IgG concentrations: (A) Quigley et al., 2013 (r=0.75; p<0.01; n=183), and (B) Elsohaby et al., 2017 (r=0.72; p<0.001; n=240), fitting the original empirical data to the model (retrospective prediction) reveals that most IgG concentrations are within the range set by the “cut-off” ˚Bx 21. The graphs indicate the upper and lower limit of the range of IgG concentrations and the median for each ˚Bx value. The IgG concentration range associated with ˚Bx 21 is shaded across the entire ˚Bx value range. In (A), the IgG concentration range for ˚Bx 21 was not distinctive, and is calculated to recognize only with a ~54.5% probability, the desired level of ≥50 g/L IgG concentration; this was almost identical in ˚Bx 20, but could not be examined for ˚Bx 19 and ˚Bx 18 due to lack of sample size. IgG concentrations for samples that tested ˚Bx 16 were still completely within the range identified for ˚Bx 21. Only 3 samples (emphasized with red) showed IgG concentrations lower than the range for ˚Bx 21. At sample sizes included for ˚Bx ≥24, all IgG concentration measurements were above 50 g/L IgG, and appeared to be least perturbed by the magnitude of residuals. This was not the case in (B), where a large subset of samples representing a wide range of ˚Bx values (from a low 11 to as high as 32) contained samples that were below 50 g/L IgG (emphasized with green for ˚Bx >21). Similar to (A), IgG concentration range for ˚Bx 21 in (B) was not distinctive, and is calculated to recognize only with a ~57% probability, the desired level of ≥50 g/L IgG concentration. Higher ˚Bx did not amount to higher IgG concentrations, as all samples in ˚Bx as high as 25 were still completely within the IgG concentration range identified for ˚Bx 21. These severe limitations integral to these models in (A) and (B), and the inconsistencies between them highlight their dubious value in prospective predictions with new ˚Bx data.