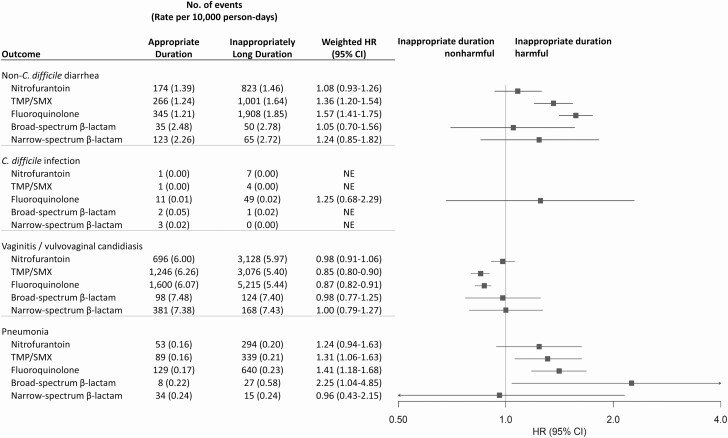
Figure 3.
Propensity score–weighted HR estimates of potential microbiome-related adverse events associated with antibiotic agents among patients prescribed guideline-recommended duration versus inappropriately long duration. Antibiotic duration was categorized as appropriate guideline-recommended duration (3 days for fluoroquinolones and TMP/SMX, 5 days for nitrofurantoin, 3–7 days for β-lactams) or inappropriately long duration; patients with inappropriately short duration were excluded. Propensity score weighting was implemented using standardized mortality ratio weighting wherein patients were weighted to reflect the covariate distribution in the patients who received appropriate guideline-recommended duration. Estimates were adjusted for age, month of prescription, year of prescription, geographic region, provider specialty, alcohol or drug abuse, deficiency anemias, chronic pulmonary disease, depression, hypertension, obesity, and psychoses. For HR estimation, we required 5 or more adverse event cases in both the reference antibiotic treatment group (ie, nitrofurantoin) and the comparator treatment group to ensure stability of the effect estimate. Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; TMP/SMX, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.