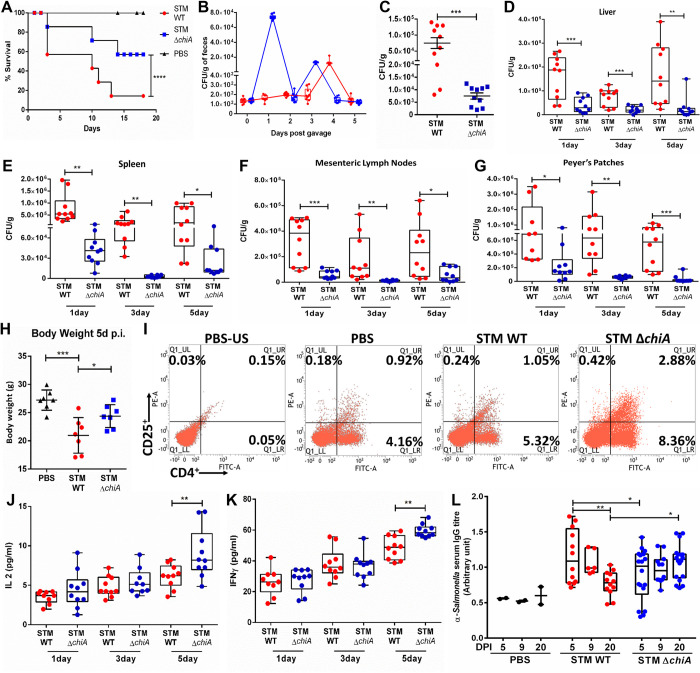
Fig 5. Chitinase facilitates in vivo invasion, survival, and pathogenesis of Salmonella Typhimurium.
(A) Survival of the mice infected with a lethal dose of STM WT and STM ΔchiA (PBS = Phosphate Buffered Saline). Data are presented from one independent experiment, representative of 3 independent experiments (N = 3). (B) Bacterial shedding in the feces of STM WT and STM ΔchiA infected animals. Data are presented as mean ± SD of 3 independent experiment; each dot represents an individual animal (N = 3, n = 10). (C) In vivo invasion in PP by STM WT and STM ΔchiA. (N = 3). Bacterial burden in (D) liver, (E) spleen, (F) MLN and (G) PP of the infected mice after the indicated time with a sub-lethal dose of STM WT and STM ΔchiA. (N = 3). Unpaired Student’s t test was used to analyze the data for C-G. (H) Body weight of the infected mice 5 dpi with a sub-lethal dose of STM WT and STM ΔchiA. (N = 3). (PBS- Phosphate Buffered Saline). (I) Flow cytometry analysis of CD4+ and CD25+ T cells from total splenocytes isolated from STM WT and STM ΔchiA infected mice 20 dpi (US-PBS- Unstained splenocytes from PBS treated mouse). Data are presented from one independent experiment, representative of 3 independent experiments (N = 3). Pro-inflammatory cytokines (J) IL-2 and (K) IFN-γ level in serum from STM WT and STM ΔchiA infected mice after the indicated time. (N = 3); One-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data. (L) Serum anti-Salmonella antibody titer was quantified by sandwich ELISA after the indicated time. (N = 3); Two-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data.