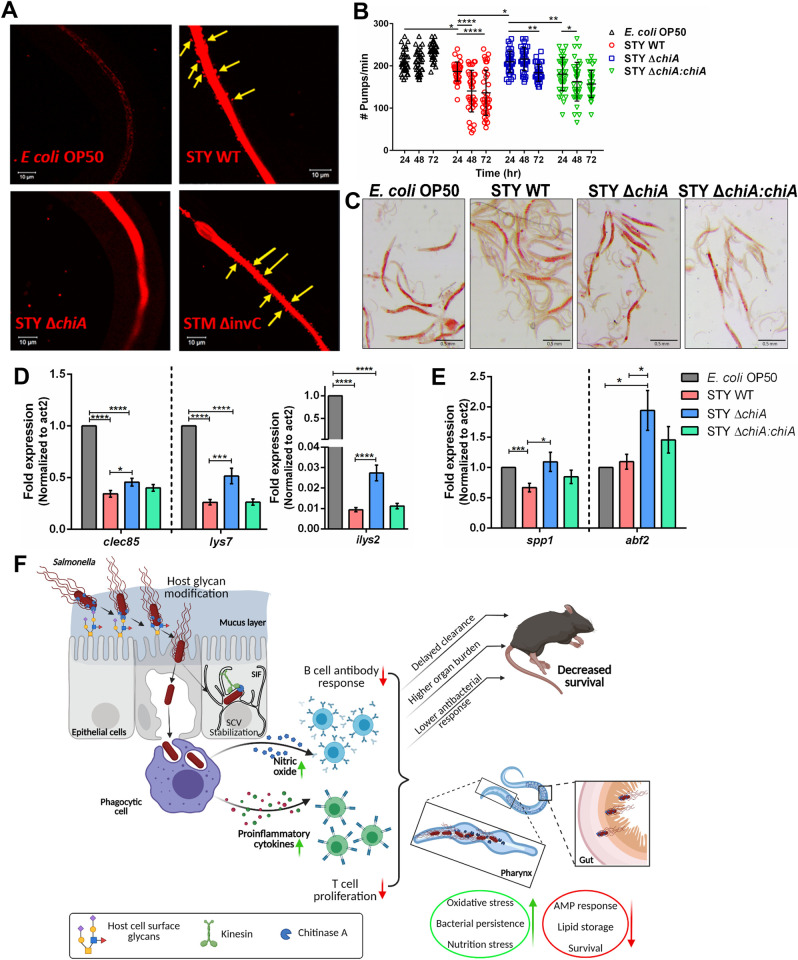
Fig 7. Salmonella chitinase is important for alteration of metabolism and antibacterial defense in C. elegans.
(A) Representative images of bacterial colonization of the worms’ gut at higher magnification. Yellow arrows show the presence of the STY WT and STM ΔinvC bacteria outside the gut lumen. (B) Quantification of no. of pharyngeal pumps/min of the worms at the indicated time. Data are represented as mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments (N = 3); Two-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data. (C) Representative images of Oil Red O (ORO) stained worms fed with different bacterial strains for 48 hours. (D, E) Quantitative RTPCR analysis of the p38 MAPK dependent antimicrobial peptide genes (D) clec85, lys7, ilys2 and (E) spp1 and abf2 in worms fed with different bacterial strains for 48 hours. Fold change was normalized over act2. (N = 4). One-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data. (F) Model depicting the role of Chitinase A in bacterial invasion and regulation of host immune response during Salmonella pathogenesis in mouse and C. elegans host (created with Biorender.com).