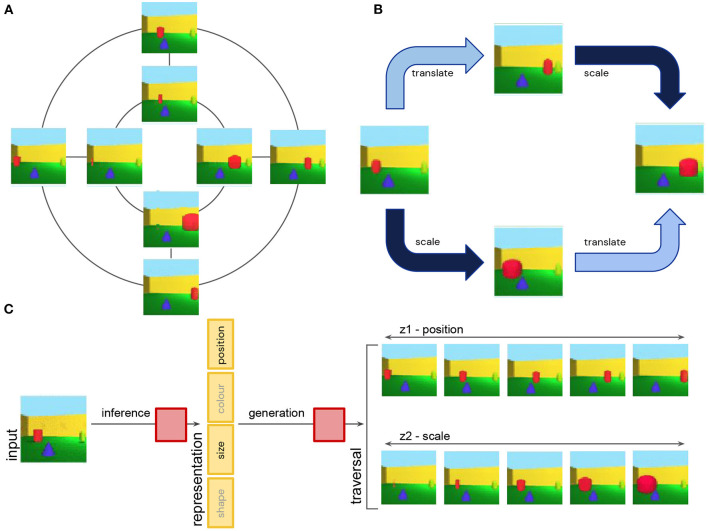
Figure 5.
(A) Simplified schematic showing discrete approximation of continuous translation and scale symmetries of 3D objects. Translations are applied along the inner and outer circles. Scale transformations are applied along straight lines. (B) Translation and scale transformation commute with each other. They can be applied in permuted order without affecting the final state. (C) Disentangling neural networks learn to infer a representation of an image that is a concatenation of independent subspaces, each one being (approximately) equivariant to a single symmetry transformation. The model uses inference to obtain a low-dimensional representation of an image, and generation to reconstruct the original image from the representation. Two example latent traversals demonstrate the effect on the image reconstruction of smoothly varying the value of the position and size subspaces.