Fig. 1.
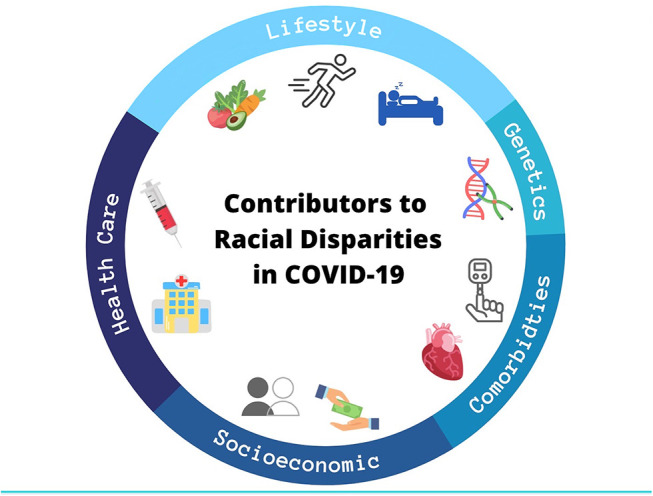
Illustration of the multi-factorial etiology of racial disparities in COVID-19 health outcomes. Though overlap among these factors exists, lower socioeconomic status and segregation/discrimination, inequities in healthcare and vaccine status, health behaviors, (epi)genetic and environmaental variation, and an increased burden of comorbidities such as cardiovascular and metabolic disease synergize to increase the prevalence and severity of COVID-19 among racial and ethnic minorities. This figure is also depicted in our companion paper.7 Resused with permission.
