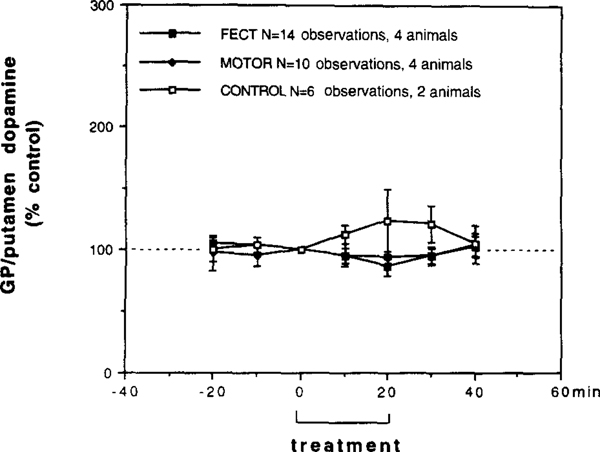
Fig. 4.
Behavioral tests on the extracellular levels of dopamine in the lateral GP/putamen (GP: globus pallidus) of narcoleptic (n=4) and control canines (n=2) measured by in vivo microdialysis. FECT treav ment represents data from seven bilateral microdialysis sessions in four narcoleptic canines (each animal tested 2 times = 14 total obervations), MOTOR treatment represents data from five bilateral microdialysis sessions in four narcoleptic canines (three animals tested I time, one animal tested 2 times =10 total observations) and CONTROL treatment represents data from three bilateral microdialysis sessions in two control canines (one animal tested onc time, one animal tested 2 times =6 total observations). During FECT treatment each animal performed two FECT trials per min, during MOTOR treatment each animal performed two MOTOR activity trails without having cataplexy per 10 min and during CONTROL treatment each animal performed two FECT trials per 10 min (no cataplexy occurred). Within each group the treatment and post-treatment time points were compared with pretreatment time points (Fishers PLSD post-hoc test). No significant differences were found.