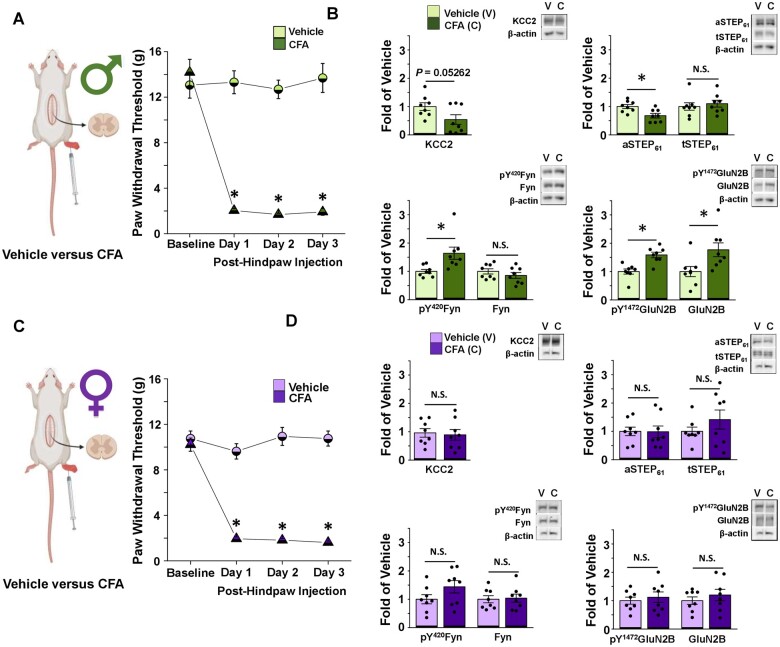
Figure 1.
CFA elicits tactile allodynia in male and female adult rats, but only activates the STEP61/pFyn/pGluN2B spinal hyperexcitability pathway at male SDH synapses. (A) Left: In vivo CFA inflammatory pain model, created using BioRender.com. Right: CFA elicits tactile allodynia in adult male rats. Von Frey behaviour testing shows that rats with a CFA injection (n = 14) to their right hindpaw have decreased PWT compared to vehicle-injected animals (n = 8; one-way repeated-measures ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni-adjusted pairwise comparisons when P < 0.05). Animal tissue was collected for use in either western blot analysis or electrophysiological recordings. (B) CFA inflammatory pain model drives upregulation of pFyn, pGluN2B, GluN2B and downregulation of aSTEP61 in male rat SDH synaptosomes. Plots (left) and representative western blots (right) from SDH synaptosomes of male rats 5 days after hindpaw injection of either vehicle (light green, n = 8 for all targets) or CFA (dark green, n = 8 for all targets; compared using independent samples t-test). (C) Left: In vivo CFA inflammatory pain model, created using Biorender.com. Right: Von Frey behaviour testing shows that rats with a CFA (n = 14) injection to their right hindpaw have decreased PWT compared to vehicle injected animals (n = 8; one-way repeated-measures ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni-adjusted pairwise comparisons when P < 0.05). Animal tissue was collected for use in either western blot analysis or electrophysiological recordings. (D) CFA inflammatory pain model elicits no effect in the STEP61/pFyn/pGluN2B spinal hyperexcitability pathway of female rat SDH synaptosomes. Plots (left) and representative western blots (right) from SDH synaptosomes of female rats 5 days after injection of either vehicle (lilac, n = 8) or CFA (purple, n = 8; compared using independent samples t-test). *P < 0.05.