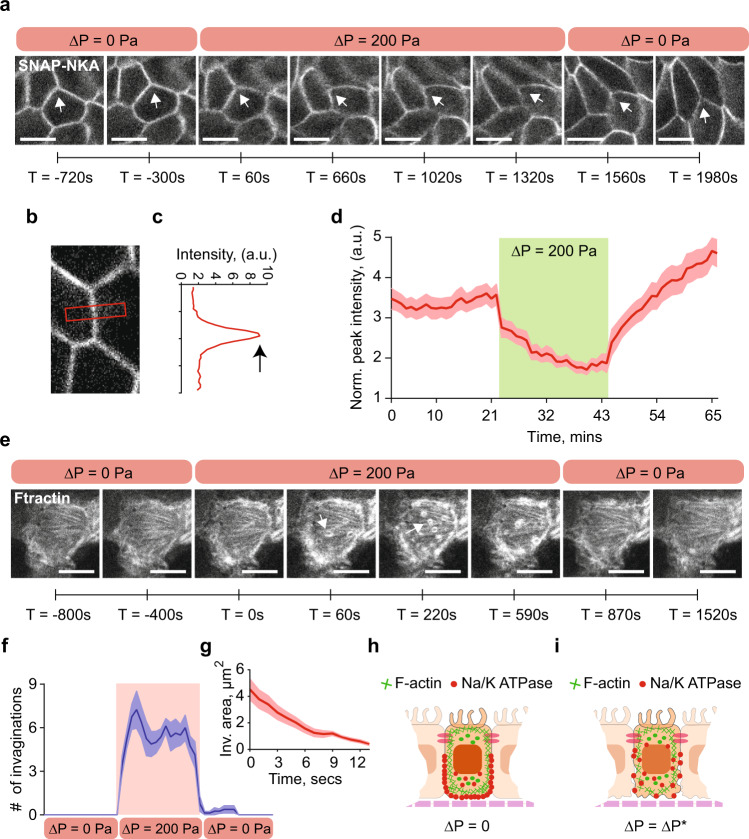
Fig. 3. ΔP decreases baso-lateral Na+/K+ ATPase localization by disrupting F-actin cortex.
a Live cell imaging MDCK-II cells stably expressing SNAP-tagged Na+/K+ ATPase (NKA) a-subunit and stained with TMR-STAR dye in the MFKP. Time-lapsed confocal images of cells’ lateral side in three consecutive conditions: zero pressure (ΔP = 0), pressure gradient (ΔP = 200 Pa) and pressure released (ΔP = 0). The arrowhead indicates disruption of lateral NKA expression in regions of interest (ROIs) at various time stamps. Scale bar = 10 mm. b A zoomed confocal slice of an ROI in MDCK-II cells expressing SNAP-tagged NKA and stained with TMR-STAR dye. c NKA intensity is quantified in a red band centered between two cells in b. The intensity profile in c is the vertical average intensity along the red box in b, the peak (indicated by black arrow) is the maximum intensity of NKA. d Mean of normalized peak lateral NKA intensity for the same cell over the course of three pressure conditions in a. Shading represents the SEM. (n = 25, N = 3, cells, biological replicates). e Live cell imaging of transiently transfected MDCK-II cells expressing GFP-tagged F-actin (Ftractin). Time-lapsed confocal images of the baso-lateral side of the cells were taken under three consecutive conditions: ΔP = 0, ΔP = 200 Pa, and pressure released (ΔP = 0). Scale bar = 10 mm. Pressure application induces rapid high-frequency invaginations in the baso-lateral domain. White arrowhead indicates F-actin rings, which are cross-section of invaginations. f Number of invaginations per unit cell over the course of three pressure conditions in e (n = 8, N = 3, cells, biological replicates). g Mean area of invaginations as a function of time under pressure. Shading represents the SEM. (n = 10, N = 3, cells, biological replicates). The invaginations have an average lifetime of ~15 s and disappear when pressure is released as shown in f. h Schematic showing co-localization of F-actin (green lines) and NKA (red dots) in cells in MFKP at ΔP = 0. i Hydrostatic pressure gradient results in high-frequency invaginations on the baso-lateral F-actin cortex and a reduction in NKA localization in the lateral domain.